Difference between revisions of "Category:612 Impact Attenuators"
m (Per EPS, revision supports the reclassification in the QPL; revision also provides guidance on when WZ crash cushions are to be used and when to reference the QPL for approved devices. Sand barrels do not fit in every project and WZ crash cushions are the alternative.) |
(updated per RR3849) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <div style="float: right; margin-left: 30px; margin-bottom: 30px;">__TOC__</div> | |
| − | {|style=" | + | {| style="background-color:#f6f6f6;" |
| − | | | + | |<gallery mode="nolines" widths=425px heights=350px> |
| − | + | File:TMA_01.png| | |
| − | |- | + | File:TMA_02.png| |
| − | |''' | + | </gallery> |
| − | + | |- style="text-align:center;" | |
| − | + | | <big>'''Protective vehicle with a truck-Mounted Attenuator and Flashing Arrow Panel'''</big> | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | Impact attenuators are designed to absorb energy of an impacting vehicle and reduce the force on a passenger. Types of impact attenuators include: truck -mounted attenuators (TMA), freestanding impact attenuators (sand barrels), and work zone crash cushions. | ||
| + | ==612.1 Truck-Mounted Attenuators== | ||
| + | Truck-mounted attenuators (TMAs) are energy-absorbing devices attached to the rear of appropriate protective vehicle. The protective vehicle that supports the TMA must meet manufacturer specifications. | ||
| + | The National Cooperative Highway Research Project 350 (NCHRP 350) and the 2016 AASHTO Manual for Assessing Safety Hardware (MASH 2016) set the crash criteria for TMAs. Non MASH 2016 impact attenuators manufactured prior to January 1, 2023 may be used until January 1, 2030. All impact attenuators manufactured after January 1, 2023 shall meet MASH 2016 Test Level 3 crash test requirements. | ||
| + | Damaged TMAs are to be removed from service and either repaired or replaced. | ||
| − | + | ===612.1.1 MoDOT TMA Marking, Emergency Alert Lights, and Audible Alert System=== | |
| + | While in the operating position, the rear facing of the TMA shall be marked with alternating 8-inch yellow and 8-inch black retroreflective sheeting forming an inverted “V” at the center and slope downward at an angle of 45 degrees toward each side of the unit or a checkered board pattern consisting of 12- inch square red and 12-inch square white retroreflective sheeting. The TMA may be marked with the same operating pattern or red and white DOT conspicuity tape to simulate the looks of a standard van body trailer when traveling. | ||
| − | + | Emergency Alert Lights (EALs) and Audible Alert systems on MoDOT MASH 2016 tested TMAs are used in accordance with typical applications. | |
| − | + | All lighting should be appropriately set, depending on the day or nighttime conditions. | |
| + | ===612.1.2 TMA Operations=== | ||
| + | ====612.1.2.1 Construction Projects==== | ||
| + | For construction projects, the use of a stationary TMA may be required on the temporary traffic control plans above and beyond the requirements of the MUTCD. If the use of a stationary TMA is required, the stationary TMA should be included on the temporary traffic control plans, contain the appropriate bid item as well as the applicable JSP for Truck Mounted Attenuator for Stationary Activities. | ||
| − | + | For construction projects, TMAs required for mobile operations, such as striping, are considered incidental per Sec 612.5. | |
| − | + | ====612.1.2.2 MoDOT Operations==== | |
| + | During MoDOT stationary operations, it is recommended the operator not wait inside or near the TMA vehicle. | ||
| − | + | During MoDOT short duration and mobile operations, TMA operators are allowed to take preventive action by rolling ahead when they perceive possible interaction with an errant vehicle. All TMAs, except TMA#1 are allowed take preventive action. | |
| − | + | ===612.1.3 MoDOT TMA Operator’s Training=== | |
| − | + | MoDOT operators are required complete MoDOT’s Truck-Trailer Mounted Attenuator (TMA) Protective Vehicle training (both classroom and On The Job training) in advance operating a TMA. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Truck | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==612.2 Impact Attenuator Array (Sand Barrels)== | |
| − | : | + | [[image:612.2 Sand Barrels.jpg|right|225px|<center>'''Sand Barrels'''</center>]] |
| − | + | An Impact Attenuator Array (Sand Barrels) is most often used to shield fixed objects that cannot be removed or relocated, when posted speeds are greater than 35 mph. These devices are recommended for temporary usage such as in work zones. A benefit/cost analysis is to be conducted before sand barrels are used in a permanent application. | |
| − | [ | + | An Impact Attenuator Array (Sand Barrels) consists of a group of freestanding plastic barrels configured in an array of increasing weights from the impact point toward the object. Such an array transfers the vehicle’s momentum to the increasing masses of sand in the barrels and provides a gradual deceleration. Each barrel is designed with a specific weight of sand to absorb the energy of an errant vehicle. The sand barrel array's "footprint" length and width and the number of barrels will change based upon the permanent posted speed limit of the roadway. For the correct setup and array of sand barrel impact attenuators, refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations. For more information about manufacturer’s recommendations, see [http://www.modot.org/business/standards_and_specs/endterminals.htm End Terminals, Crash Cushions and Barrier Systems]. |
| − | + | The pay item will be based on the posted speed limit for the location the sand barrels will be used. Each Impact Attenuator XX mph (Sand Barrel Array) will be paid for per each, as a unit including the number of barrels and weight of sand in each barrel, as required by the manufacturer. If it is anticipated that the sand barrel array will be relocated during staged construction, the entire array will be relocated and paid for by the pay item Impact Attenuator (Relocation) each time the sand barrel array is relocated. The relocated array should be used in an area with the same posted speed limit, or another pay item will need to be used. An estimate for replacement barrels needs to be included as a separate pay item, typically calculated as one for each sand barrel array. No direct payment is made for the Type 1 object marker on the lead sand barrel in the array. | |
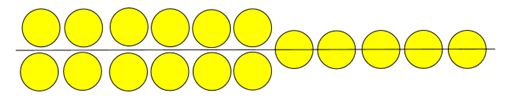
[[image:612.2 array.jpg|center|<center>'''Typical Array for Sand-Filled Impact Attenuators | [[image:612.2 array.jpg|center|<center>'''Typical Array for Sand-Filled Impact Attenuators | ||
May Change Based on Manufacturer’s Recommendations'''</center>]] | May Change Based on Manufacturer’s Recommendations'''</center>]] | ||
| + | ==612.3 Work Zone Crash Cushion== | ||
| − | + | Work Zone Crash Cushions are used to protect traffic from the blunt end of temporary barrier curb. A crash cushion will be required on the upstream end of barrier curb for divided facilities, and on both ends for all two-way facilities. When space allows, sand barrel impact attenuators are the preferred choice for temporary protection. However, in the event that sand barrels cannot be used (for example, insufficient width), work zone crash cushions may be used instead. Work zone crash cushions provide a narrower option than sand barrels, but still perform the same function. Work zone crash cushions are discussed in [[617.1_Temporary_Traffic_Barriers#617.1.3.3_Crash_Cushion|EPG 617.1.3.3 Crash Cushion]]. Applicable pay items are included in the plans. | |
| − | + | ==612.4 Construction Inspection Guidelines== | |
| − | + | '''Material (for Sec 612.2)''' Certifications are to be collected on retroreflective sheeting and any other product specified in Sec 1063. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Safety Requirements (for Sec 612.3)''' The inspector is to request a copy of the manufacturer’s certification that states the units comply with the crash test requirements of NCHRP 350 or MASH 2016, Test Level 3. This information is to be kept in the project files. | |
| − | ''' | + | '''Truck-Mounted Attenuator (for Sec 612.4.1)''' TMAs are to be inspected to make sure they are structurally sound, the frames are not bent and that they appear to be in good working order. In some cases, the contractor may elect to add TMAs when TMAs are not required. Elective TMAs need to be NCHRP 350 or MASH 2016, Test Level 3 compliant and therefore the certification still needs to be collected. |
| − | ''' | + | '''Sand-Filled Impact Attenuator Array (for Sec 612.4.2)''' The inspector is to request a copy of the manufacturer’s installation instructions for the particular brand of sand-filled impact attenuator the contractor is using. The use of more than one manufacturer’s sand barrels in an array is not allowed. When inspecting the sand-filled impact attenuator arrays, make sure that the array is in the location as shown in the temporary traffic control plans, and set up and filled in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. All lids are to be on and secured. In order to prevent the sand inside the barrels from freezing in cold weather, the sand shall have a maximum moisture content and rock salt added, according to Sec 612.4.2.1. The contractor should provide the calculations for moisture content and rock salt content for each barrel, so the specification requirements can be verified. When checking the contents of the barrels, rock salt should be visible in the sand mix, to verify uniform dispersion in the sand. During periods of extended cold weather, the sand should be checked periodically to make sure it has not frozen because the salt content has been exhausted. If this condition is found, the contractor will need to add more salt or replace the sand/salt mixture. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''Work Zone Crash Cushions (for Sec 612.4.3).''' The inspector is to request a copy of the manufacturer’s installation instructions for the particular brand of crash cushion the contractor is using. When inspecting the work zone crash cushion, make sure that the crash cushion is in the location as shown on the temporary traffic control plans and set up in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. If the crash cushion is water-filled, MoDOT requires a mixture content per manufacturer’s recommendations so that the crash cushion will not freeze and create a safety hazard. During periods of extended cold weather, the crash cushion(s) should be checked periodically to make sure it has not frozen. If this condition is found, the contractor will need to correct and/or replace the mixture. In the event the work zone crash cushion is damaged and needs to be replaced, it is considered incidental and replaced at no cost to the Commission. | '''Work Zone Crash Cushions (for Sec 612.4.3).''' The inspector is to request a copy of the manufacturer’s installation instructions for the particular brand of crash cushion the contractor is using. When inspecting the work zone crash cushion, make sure that the crash cushion is in the location as shown on the temporary traffic control plans and set up in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. If the crash cushion is water-filled, MoDOT requires a mixture content per manufacturer’s recommendations so that the crash cushion will not freeze and create a safety hazard. During periods of extended cold weather, the crash cushion(s) should be checked periodically to make sure it has not frozen. If this condition is found, the contractor will need to correct and/or replace the mixture. In the event the work zone crash cushion is damaged and needs to be replaced, it is considered incidental and replaced at no cost to the Commission. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:53, 3 May 2024
| Protective vehicle with a truck-Mounted Attenuator and Flashing Arrow Panel |
Impact attenuators are designed to absorb energy of an impacting vehicle and reduce the force on a passenger. Types of impact attenuators include: truck -mounted attenuators (TMA), freestanding impact attenuators (sand barrels), and work zone crash cushions.
612.1 Truck-Mounted Attenuators
Truck-mounted attenuators (TMAs) are energy-absorbing devices attached to the rear of appropriate protective vehicle. The protective vehicle that supports the TMA must meet manufacturer specifications.
The National Cooperative Highway Research Project 350 (NCHRP 350) and the 2016 AASHTO Manual for Assessing Safety Hardware (MASH 2016) set the crash criteria for TMAs. Non MASH 2016 impact attenuators manufactured prior to January 1, 2023 may be used until January 1, 2030. All impact attenuators manufactured after January 1, 2023 shall meet MASH 2016 Test Level 3 crash test requirements.
Damaged TMAs are to be removed from service and either repaired or replaced.
612.1.1 MoDOT TMA Marking, Emergency Alert Lights, and Audible Alert System
While in the operating position, the rear facing of the TMA shall be marked with alternating 8-inch yellow and 8-inch black retroreflective sheeting forming an inverted “V” at the center and slope downward at an angle of 45 degrees toward each side of the unit or a checkered board pattern consisting of 12- inch square red and 12-inch square white retroreflective sheeting. The TMA may be marked with the same operating pattern or red and white DOT conspicuity tape to simulate the looks of a standard van body trailer when traveling.
Emergency Alert Lights (EALs) and Audible Alert systems on MoDOT MASH 2016 tested TMAs are used in accordance with typical applications.
All lighting should be appropriately set, depending on the day or nighttime conditions.
612.1.2 TMA Operations
612.1.2.1 Construction Projects
For construction projects, the use of a stationary TMA may be required on the temporary traffic control plans above and beyond the requirements of the MUTCD. If the use of a stationary TMA is required, the stationary TMA should be included on the temporary traffic control plans, contain the appropriate bid item as well as the applicable JSP for Truck Mounted Attenuator for Stationary Activities.
For construction projects, TMAs required for mobile operations, such as striping, are considered incidental per Sec 612.5.
612.1.2.2 MoDOT Operations
During MoDOT stationary operations, it is recommended the operator not wait inside or near the TMA vehicle.
During MoDOT short duration and mobile operations, TMA operators are allowed to take preventive action by rolling ahead when they perceive possible interaction with an errant vehicle. All TMAs, except TMA#1 are allowed take preventive action.
612.1.3 MoDOT TMA Operator’s Training
MoDOT operators are required complete MoDOT’s Truck-Trailer Mounted Attenuator (TMA) Protective Vehicle training (both classroom and On The Job training) in advance operating a TMA.
612.2 Impact Attenuator Array (Sand Barrels)
An Impact Attenuator Array (Sand Barrels) is most often used to shield fixed objects that cannot be removed or relocated, when posted speeds are greater than 35 mph. These devices are recommended for temporary usage such as in work zones. A benefit/cost analysis is to be conducted before sand barrels are used in a permanent application.
An Impact Attenuator Array (Sand Barrels) consists of a group of freestanding plastic barrels configured in an array of increasing weights from the impact point toward the object. Such an array transfers the vehicle’s momentum to the increasing masses of sand in the barrels and provides a gradual deceleration. Each barrel is designed with a specific weight of sand to absorb the energy of an errant vehicle. The sand barrel array's "footprint" length and width and the number of barrels will change based upon the permanent posted speed limit of the roadway. For the correct setup and array of sand barrel impact attenuators, refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations. For more information about manufacturer’s recommendations, see End Terminals, Crash Cushions and Barrier Systems.
The pay item will be based on the posted speed limit for the location the sand barrels will be used. Each Impact Attenuator XX mph (Sand Barrel Array) will be paid for per each, as a unit including the number of barrels and weight of sand in each barrel, as required by the manufacturer. If it is anticipated that the sand barrel array will be relocated during staged construction, the entire array will be relocated and paid for by the pay item Impact Attenuator (Relocation) each time the sand barrel array is relocated. The relocated array should be used in an area with the same posted speed limit, or another pay item will need to be used. An estimate for replacement barrels needs to be included as a separate pay item, typically calculated as one for each sand barrel array. No direct payment is made for the Type 1 object marker on the lead sand barrel in the array.
612.3 Work Zone Crash Cushion
Work Zone Crash Cushions are used to protect traffic from the blunt end of temporary barrier curb. A crash cushion will be required on the upstream end of barrier curb for divided facilities, and on both ends for all two-way facilities. When space allows, sand barrel impact attenuators are the preferred choice for temporary protection. However, in the event that sand barrels cannot be used (for example, insufficient width), work zone crash cushions may be used instead. Work zone crash cushions provide a narrower option than sand barrels, but still perform the same function. Work zone crash cushions are discussed in EPG 617.1.3.3 Crash Cushion. Applicable pay items are included in the plans.
612.4 Construction Inspection Guidelines
Material (for Sec 612.2) Certifications are to be collected on retroreflective sheeting and any other product specified in Sec 1063.
Safety Requirements (for Sec 612.3) The inspector is to request a copy of the manufacturer’s certification that states the units comply with the crash test requirements of NCHRP 350 or MASH 2016, Test Level 3. This information is to be kept in the project files.
Truck-Mounted Attenuator (for Sec 612.4.1) TMAs are to be inspected to make sure they are structurally sound, the frames are not bent and that they appear to be in good working order. In some cases, the contractor may elect to add TMAs when TMAs are not required. Elective TMAs need to be NCHRP 350 or MASH 2016, Test Level 3 compliant and therefore the certification still needs to be collected.
Sand-Filled Impact Attenuator Array (for Sec 612.4.2) The inspector is to request a copy of the manufacturer’s installation instructions for the particular brand of sand-filled impact attenuator the contractor is using. The use of more than one manufacturer’s sand barrels in an array is not allowed. When inspecting the sand-filled impact attenuator arrays, make sure that the array is in the location as shown in the temporary traffic control plans, and set up and filled in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. All lids are to be on and secured. In order to prevent the sand inside the barrels from freezing in cold weather, the sand shall have a maximum moisture content and rock salt added, according to Sec 612.4.2.1. The contractor should provide the calculations for moisture content and rock salt content for each barrel, so the specification requirements can be verified. When checking the contents of the barrels, rock salt should be visible in the sand mix, to verify uniform dispersion in the sand. During periods of extended cold weather, the sand should be checked periodically to make sure it has not frozen because the salt content has been exhausted. If this condition is found, the contractor will need to add more salt or replace the sand/salt mixture.
Work Zone Crash Cushions (for Sec 612.4.3). The inspector is to request a copy of the manufacturer’s installation instructions for the particular brand of crash cushion the contractor is using. When inspecting the work zone crash cushion, make sure that the crash cushion is in the location as shown on the temporary traffic control plans and set up in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. If the crash cushion is water-filled, MoDOT requires a mixture content per manufacturer’s recommendations so that the crash cushion will not freeze and create a safety hazard. During periods of extended cold weather, the crash cushion(s) should be checked periodically to make sure it has not frozen. If this condition is found, the contractor will need to correct and/or replace the mixture. In the event the work zone crash cushion is damaged and needs to be replaced, it is considered incidental and replaced at no cost to the Commission.
This category currently contains no pages or media.