903.7 Conventional Road Guide Signs
Contents
- 1 903.7.1 Scope of Conventional Road Guide Sign Standards (MUTCD Section 2D.01)
- 2 903.7.2 Application (MUTCD Section 2D.02)
- 3 903.7.3 Color, Retroreflection, and Illumination (MUTCD Section 2D.03)
- 4 903.7.4 Size of Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.04)
- 5 903.7.5 Lettering Style (MUTCD Section 2D.05)
- 6 903.7.6 Size of Lettering (MUTCD Section 2D.06)
- 7 903.7.7 Amount of Legend (MUTCD Section 2D.07)
- 8 903.7.8 Arrows (MUTCD Section 2D.08)
- 9 903.7.9 Numbered Highway Systems (MUTCD Section 2D.09)
- 10 903.7.10 Route Signs and Auxiliary Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.10)
- 11 903.7.11 Design of Route Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.11)
- 12 903.7.12 Design of Route Sign Auxiliaries (MUTCD Section 2D.12)
- 13 903.7.13 Junction Auxiliary Sign (M2-1) (MUTCD Section 2D.13)
- 14 903.7.14 Cardinal Direction Auxiliary Signs (M3-1 through M3-4) (MUTCD Section 2D.15)
- 15 903.7.15 Auxiliary Signs for Alternative Routes (M4 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.16)
- 16 903.7.16 ALTERNATE Auxiliary Signs (M4-1) (MUTCD Section 2D.17)
- 17 903.7.17 SPUR Auxiliary Sign (M4-1b)
- 18 903.7.18 BUSINESS Auxiliary Sign (M4-3) (MUTCD Section 2D.19)
- 19 903.7.19 TO Auxiliary Sign (M4-5) (MUTCD Section 2D.21)
- 20 903.7.20 END Auxiliary Sign (M4-6) (MUTCD Section 2D.22)
- 21 903.7.21 TEMPORARY Auxiliary Signs (M4-7) (MUTCD Section 2D.24)
- 22 903.7.22 Temporary Detour and Auxiliary Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.25)
- 23 903.7.23 Advance Turn Arrow Auxiliary Signs (M5-1, M5-2, M5-3) (MUTCD Section 2D.26)
- 24 903.7.24 Lane Designation Auxiliary Signs (M5-4, M5-5, M5-6) (MUTCD Section 2D.27)
- 25 903.7.25 Directional Arrow Auxiliary Signs (M6 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.28)
- 26 903.7.26 Route Sign Assemblies (MUTCD Section 2D.29)
- 27 903.7.27 Junction Assembly (MUTCD Section 2D.30)
- 28 903.7.28 Advance Route Turn Assembly (MUTCD Section 2D.31)
- 29 903.7.29 Directional Assembly (MUTCD Section 2D.32)
- 30 903.7.30 Combination Lane-Use/Destination Overhead Guide Sign (MUTCD Section 2D.33)
- 31 903.7.31 Confirming or Reassurance Assemblies (MUTCD Section 2D.34)
- 32 903.7.32 Trailblazer Assembly (MUTCD Section 2D.35)
- 33 903.7.33 Destination and/or Distance Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.36)
- 34 903.7.34 Destination Signs (D1 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.37)
- 35 903.7.35 Destination Signs at Circular Intersections (MUTCD Section 2D.38)
- 36 903.7.36 Destination Signs at Jughandles (MUTCD Section 2D.39)
- 37 903.7.37 Location of Destination Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.40)
- 38 903.7.38 Distance Signs (D2 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.41)
- 39 903.7.39 Location of Distance Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.42)
- 40 903.7.40 Destination and Distance Signs (D1a Series)
- 41 903.7.41 Street Name Signs (D3-1 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.43)
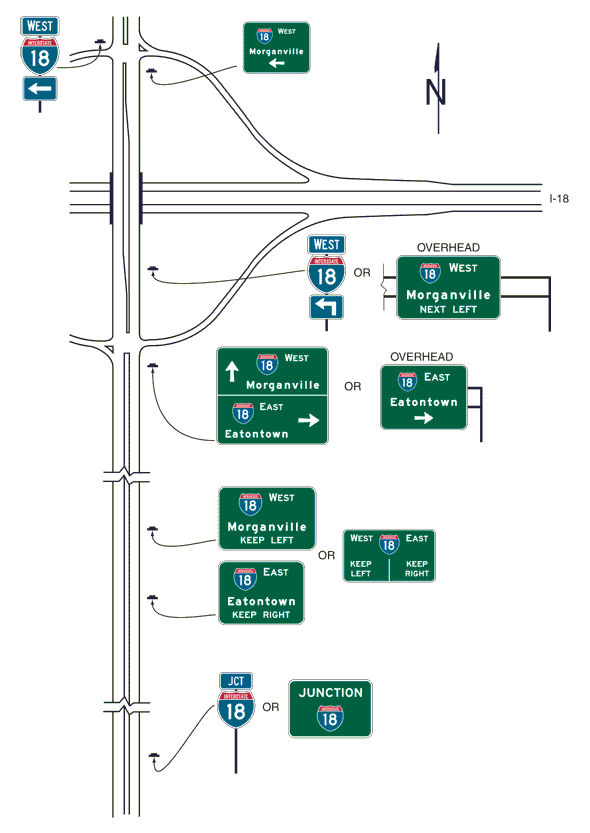
- 42 903.7.42 Advance Street Name Signs (D3-2 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.44)
- 43 903.7.43 Signing on Conventional Roads on Approaches to Interchanges (MUTCD Section 2D.45)
- 44 903.7.44 Lake Road Signs (M1-15)
- 45 903.7.45 MoDOT Maintenance Signs (M19-1, M19-2)
- 46 903.7.46 Parking Area Guide Sign (D4-1) (MUTCD Section 2D.47)
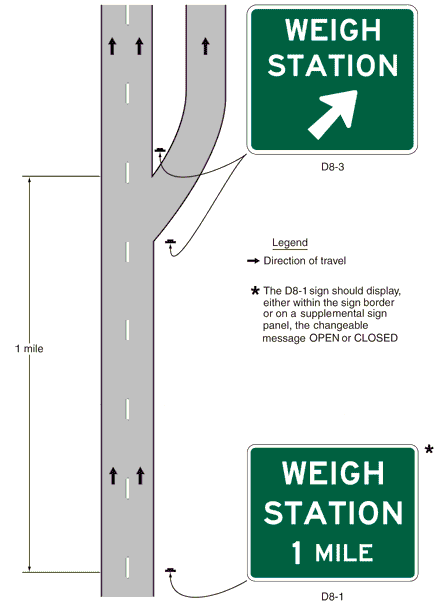
- 47 903.7.47 PARK - RIDE Sign (D4-2) (MUTCD Section 2D.48)
- 48 903.7.48 Weigh Station Signing (D8 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.49)
- 49 903.7.49 Community Wayfinding Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.50)
- 50 903.7.50 Climbing Lane Signs (D17-1, D17-2) (MUTCD Section 2D.51)
- 51 903.7.51 National Scenic Byways Signs (D6-4) (MUTCD Section 2D.55)
- 52 903.7.52 Missouri Scenic Byways Signs (D6-4b, D6-4c, D6-4d)
903.7.1 Scope of Conventional Road Guide Sign Standards (MUTCD Section 2D.01)
Standard. The provisions of this article shall apply to any road or street other than expressways and freeways.
903.7.2 Application (MUTCD Section 2D.02)
Support. Guide signs are essential to direct travelers along streets and highways, inform them of intersecting routes, direct them to cities, towns, villages or other important destinations, identify nearby rivers, parks, forests and historical sites, and give information that will help them along their way in the most simple, direct manner.
Refer to EPG 903.2 Extent of Signing for additional information on placement, location and other general criteria for signs.
903.7.3 Color, Retroreflection, and Illumination (MUTCD Section 2D.03)
Support. Requirements for illumination, retroreflection, and color are stated under the specific headings for individual guide signs or groups of signs. General provisions are provided in EPG 903.2.7 and EPG 903.2.9.
Standard. Except where otherwise provided for individual signs or groups of signs, guide signs on streets and highways shall have a white message and border on a green background. All messages, borders and legends shall be retroreflective and all backgrounds shall be retroreflective or illuminated.
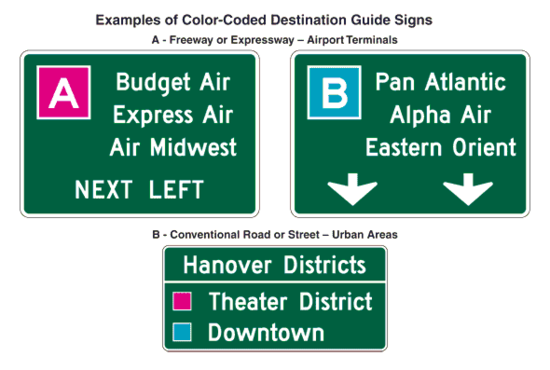
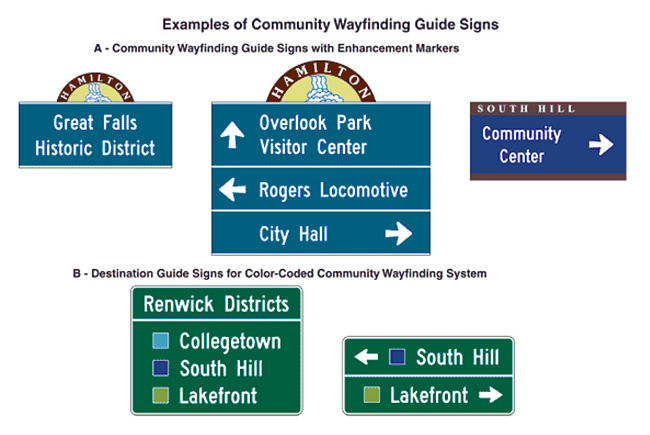
Support. Color coding is sometimes used to help road users distinguish between multiple potentially confusing destinations. Examples of valuable uses of color coding include guide signs for roadways approaching or inside an airport property with multiple terminals serving multiple airlines, and community wayfinding guide signs for various traffic generator destinations within a community or area.
Standard. Except where otherwise provided different color sign backgrounds shall not be used to provide color coding of destinations. The color coding shall be accomplished by the use of different colored square or rectangular sign panels on the face of the guide signs.
Option. The different colored sign panels may include a black or white (whichever provides the better contrast with the panel color) letter, numeral, or other appropriate designation to identify an airport terminal or other destination.
Support. Two examples of color-coded sign assemblies are shown in Fig. 903.7.3. EPG 903.7.49 contains specific provisions regarding Community Wayfinding guide signs.
903.7.4 Size of Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.04)
Standard. Except as provided in EPG 903.2.21, the sizes of conventional road guide signs that have standardized designs shall be as shown in Table 903.7.4.
Support. EPG 903.2.13 contains information regarding the applicability of the various columns in Table 903.7.4.
Option. Signs larger than those shown in Table 903.7.4 may be used.
Support. For other guide signs, the legends are so variable that a standardized design or size is not appropriate. The sign size is determined primarily by the length of the message and the size of lettering and spacing necessary for proper legibility.
Option. Reduced letter height, interline spacing, and edge spacing may be used on guide signs if sign size must be limited by factors such as lane width or vertical or lateral clearance.
Guidance. Reduced spacing between the letters or words on a line of legend should not be used as a means of reducing the overall size of a guide sign, except where determined necessary by engineering judgment to meet unusual lateral space constraints. In such cases, the legibility distance of the sign legend (refer to EPG 903.2.15) should be the primary consideration in determining whether to reduce the spacing between the letters of the words or between the words and the sign border, or to reduce the letter height.
When a reduction in the prescribed size is necessary, the design used should be as similar as possible to the design for the standard size.
Table 903.7.4 Guide Sign Sizes
| Sign or Plaque | Sign Designation | EPG Article | Conventional Road (in. x in.) | Freeway/Expressway (in. x in.) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Lane | Multi-Lane | Oversized | Mainline & Ramps | |||
| Interstate Route Sign | M1-1 | 903.7.11 | Varies X 24 | Varies X 24 | - | Varies X 24 |
| Business Loop Sign (interstate only) | M1-2 | 903.7.11 | Varies X 24 | Varies X 24 | - | Varies X 24 |
| U.S. Route Sign | M1-4 | 903.7.11 | Varies X 24 | Varies X 24 | - | Varies X 24 |
| State Number Route Sign | M1-5 | 903.7.11 | Varies X 24 | Varies X 24 | - | Varies X 24 |
| State Letter Route Sign | M1-5a | 903.7.11 | Varies X 24 | Varies X 24 | - | Varies X 24 |
| Junction | M2-1 | 903.7.13 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| NORTH | M3-1 | 903.7.14 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| EAST | M3-2 | 903.7.14 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| SOUTH | M3-3 | 903.7.14 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| WEST | M3-4 | 903.7.14 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| ALTERNATE | M4-1 | 903.7.16 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| SPUR | M4-1b | 903.7.17 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| BUSINESS | M4-3 | 903.7.18 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| TO | M4-5 | 903.7.19 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| END | M4-6 | 903.7.20 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| TEMPORARY | M4-7 | 903.7.21 | 24 X 12 | 24 X 12 | - | 24 X 12 |
| Advance Turn Arrow (90° Left/Right) | M5-1 | 903.7.23 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| Advance Turn Arrow (45° Left/Right) | M5-2 | 903.7.23 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| Directional Arrow (Left/Right) | M6-1 | 903.7.25 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| Directional Arrow (45° Left/Right) | M6-2 | 903.7.25 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| Directional Arrow (Straight) | M6-3 | 903.7.25 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| Directional Arrow (Two-Way) | M6-4 | 903.7.25 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| Directional Arrow (Two-Way 45° Left/Right) | M6-5 | 903.7.25 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| Directional Arrow (Up & Left/Right) | M6-6 | 903.7.25 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| Directional Arrow (Up & 45° Left/Right) | M6-7 | 903.7.25 | 21 X 15 | 21 X 15 | - | 21 X 15 |
| Destination (one line) | D1-1 | 903.7.34 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| Destination (two line) | D1-2 | 903.7.34 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| Destination (three line) | D1-3 | 903.7.34 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| Distance (one line) | D2-1 | 903.7.38 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| Distance (two line) | D2-2 | 903.7.38 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| Distance (three line) | D2-3 | 903.7.38 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| Destination and Distance (one line) | D1-1a | 903.7.40 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| Destination and Distance (two line) | D1-2a | 903.7.40 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| Destination and Distance (three line) | D1-3a | 903.7.40 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| Street Name (one line) | D3-1 | 903.7.41 | Varies | Varies | - | - |
| Street Name (two line) | D3-1b | 903.7.41 | Varies X 18 | Varies X 18 | - | - |
| Advance Street Name | D3-2 | 903.7.42 | Varies | Varies | - | Varies |
| MoDOT Maintenance Ends | M19-2 | 903.7.45 | 18 X 12 | - | - | - |
| Parking Area | D4-1 | 903.7.46 | 30 X 24 | 30 X 24 | - | - |
| Commuter | D4-1P | 903.7.46 | 30 X 6 | 30 X 6 | - | - |
| Commuter Parking | D4-1a | 903.7.46 | 60 X 36 | 60 X 36 | - | - |
| Park - Ride | D4-2 | 903.7.47 | 30 X 36 | 30 X 36 | - | - |
| Weigh Station _ Miles | D8-1 | 903.7.48 | 48 X 48 | 48 X 48 | - | 108 X 84 |
| Weigh Station (with arrow) | D8-3 | 903.7.48 | 48 X 48 | 48 X 48 | - | 84 X 72 |
903.7.5 Lettering Style (MUTCD Section 2D.05)
Standard. The design of upper-case letters, lower-case letters, numerals, route shields and spacing shall be as provided by the Central Office Highway Safety and Traffic Division.
The lettering for names of places, streets, and highways on conventional road guide signs shall be a combination of lower-case letters with initial upper-case letters (refer to EPG 903.2.15). The nominal loop height of the lower-case letters shall be 3/4 the height of the initial upper-case letter. When a mixed-case legend letter height is specified referring only to the initial upper-case letter, the height of the lower-case letters that follow shall be determined by this proportion. When the height of a lower-case letter is referenced, the reference is made to the nominal loop height and the height of the initial upper-case letter shall also be determined by this proportion.
All other word legends on conventional road guide signs shall be in upper-case letters.
The unique letter forms for each of the Standard Alphabet series shall not be stretched, compressed, warped, or otherwise manipulated. Modifications to the length of a word for a given letter height and series shall be accomplished only by the methods described in EPG 903.7.4.
903.7.6 Size of Lettering (MUTCD Section 2D.06)
Support. Sign legibility is a direct function of letter size and spacing. Legibility distance has to be sufficient to give travelers enough time to read and comprehend the sign. Under optimum conditions, a guide sign message can be read and understood in a brief glance. The legibility distance accounts for factors such as inattention, blocking of view by other vehicles, unfavorable weather, inferior eyesight, or other causes for delayed or slow reading. Where conditions permit, repetition of guide information on successive signs gives the traveler more than one opportunity to obtain the information needed.
Standard. Design layouts for conventional road guide signs shall be provided by Central Office Highway Safety and Traffic Division.
The principal legend on guide signs shall be in letters and numerals at least 6 inches tall for all upper-case letters, or a combination of 6 inches tall for upper-case letters and 4.5 inches tall for lower-case letters.
Guidance. Lettering sizes should be consistent on any particular class of highway.
The minimum lettering sizes provided should be exceeded where conditions indicate a need for greater legibility.
903.7.7 Amount of Legend (MUTCD Section 2D.07)
Support. The longer the legend is on a guide sign, the longer it will take travelers to comprehend it, regardless of letter size.
Guidance. Except where otherwise provided, guide signs should be limited to no more than three lines of destinations, which include place names, route numbers, street names, and cardinal directions. Where two or more signs are included in the same overhead display, the amount of legend should be further minimized. Where appropriate, a distance message or action information, such as an exit number, NEXT RIGHT, or directional arrows, should be provided on guide signs in addition to the destinations.
903.7.8 Arrows (MUTCD Section 2D.08)
Support. Arrows are used for lane assignment and to indicate the direction toward designated routes or destinations. Figure 903.7.8 shows the various standard arrow designs that have been approved for use on guide signs. Detailed drawings and standardized sizes based on ranges of letter heights for these arrows will be provided by Central Office Highway Safety and Traffic.
Standard. On overhead signs where it is desirable to indicate a lane to be followed, a down arrow shall be positioned approximately over the center of the lane and shall point vertically downward toward the approximate center of that lane. Down arrows shall be used only on overhead guide signs that restrict the use of specific lanes to traffic bound for the destination(s) and/or route(s) indicated by these arrows. Down arrows shall not be used unless an arrow can be located over and pointed to the approximate center of each lane that can be used to reach the destination displayed on the sign.
If down arrows are used, having more than one down arrow pointing to the same lane on a single overhead sign or on multiple signs on the same overhead signs structure shall not be permitted. Where a roadway is leaving the through lanes, a directional arrow shall point upward at an angle that approximates the alignment of the exit roadway.
Curved-stem arrows shall not be used on any sign that is not associated with a circular intersection.
Guidance. Arrows used on guide signs to indicate the directions toward designated routes or destinations should be pointed at the appropriate angle to clearly convey the direction to be taken. A horizontally oriented directional arrow design should be used at right-angle intersections.
On a post-mounted guide sign, a directional arrow for a straight-through movement should point upward. For a turn, the arrow on a guide sign should point horizontally or at an upward angle that approximates the sharpness of the turn.
Option. Arrows may be placed below the principal sign legend or on the appropriate side of the legend.
Guidance. At an exit, an arrow should be placed at the side of the sign that will reinforce the movement of exiting traffic. The directional arrow design should be used.
Arrows used in Overhead Arrow-per-Lane and Diagrammatic guide signing, if used on conventional roads, except for signs on approaches to roundabouts, should follow the principles set forth in EPG 903.8.33 Interchange Classification. Arrows used in Diagrammatic guide signing on approaches to roundabouts should follow the principles set forth in EPG 903.7.35.
903.7.9 Numbered Highway Systems (MUTCD Section 2D.09)
Support. The purpose of numbering and signing highway systems should identify routes and facilitate travel.
The American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) number the interstate and U.S. highway systems upon recommendations of the state highway organizations because the respective states own these systems. State and county road systems are numbered by the appropriate authorities.
The basic policy for numbering the interstate and U.S. highway systems is contained in the following Purpose and Policy statements published by AASHTO:
- A. “Establishment and Development of United States Numbered Highways”; and
- B. “Establishment of a Marking System of the Routes Comprising the National System of Interstate and Defense Highways.”
Guidance. The principles of these policies should be followed in establishing the highway systems and any other system, with effective coordination between adjacent jurisdictions. Care should be taken to avoid the use of numbers or other designations that have been assigned to interstate, U.S., or state routes in the same geographic area. Overlapping numbered routes should be kept to a minimum.
Standard. Route systems shall be given preference in this order: interstate, U.S., state and county. The preference shall be given by installing the highest-priority legend on the top or the left of the sign.
903.7.10 Route Signs and Auxiliary Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.10)
Standard. All numbered highway routes shall be identified by route signs and auxiliary signs. The signs for each system of numbered highways, which are distinctive in shape and color, shall be used only on that system and the approaches thereto.
Option. Route signs and auxiliary signs may be proportionally enlarged where greater legibility is needed.
Support. Route signs are typically mounted in assemblies with auxiliary signs. EPG 903.7.51 and EPG 903.7.52 contain information regarding the signing for scenic byways.
EPG 903.9.5 contains information regarding the signing for Auto Tour Routes.
903.7.11 Design of Route Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.11)
Standard. The MoDOT Sign Management System (SMS) Sign Catalog shall be used for designing route signs. The authority having jurisdiction shall establish other route sign designs.
Interstate Route signs (M1-1) shall consist of a cutout shield, with the route number in white letters on a blue background, the word INTERSTATE in white upper-case letters on a red background and a white border. This sign shall be used on all interstate routes and in connection with route sign assemblies on intersecting highways.
A 24 in. x 24 in. minimum sign size shall be used for interstate route numbers with one or two digits, and a 30 in. x 24 in. minimum sign size shall be used for interstate route numbers having three digits.
Off-Interstate Business Route (M1-2) signs shall consist of a cutout shield carrying the number of the connecting Interstate route and the words BUSINESS and LOOP in upper-case letters. The legend and border shall be white on a green background and the shield shall be the same shape and dimensions as the Interstate Route sign. In no instance shall the word INTERSTATE appear on the Off-Interstate Business Route sign.
Option. The Off-Interstate Business Route sign may be used on a major highway that is not a part of the Interstate system, but one that serves the business area of a city from an interchange on the system and rejoins the major highway. When used on a green guide sign, a white square or rectangle may be placed behind the shield to improve contrast.
Standard. U.S. Route (M1-4) signs shall consist of black numerals on a white shield surrounded by a black background without a border. This sign shall be used on all U.S. routes and in connection with route sign assemblies on intersecting highways.
A 24 in. x 24 in. minimum sign size shall be used for U.S. route numbers with one or two digits, and a 30 in. x 24 in. minimum sign size shall be used for U.S. route numbers having three digits.
State Numbered Route (M1-5) signs shall consist of black numerals on a white representation of the State of Missouri surrounded by a rectangular black background without a border. (A design detail is provided in Sign Detail) This sign shall be used on all state routes and in connection with route sign assemblies on intersecting highways.
A 24 in. x 24 in. minimum sign size shall be used for state numbered route numbers with one or two digits, and a 30 in. x 24 in. minimum sign size shall be used for state numbers having three digits.
State Lettered Route (M1-5a) signs shall be rectangular with the route letter in the center. The legend and border shall be black on a white background.
A 24 in. x 24 in. minimum sign size shall be used for state lettered routes with one letter and a 30 in. x 24 in. minimum sign size shall be used for state lettered routes having two letters.
Guidance. The letters G, I, L, Q and S should not be used on State Lettered Route signs. The letter R should be used on supplemental routes connecting state parks or other recreational facilities. Usually, but not always, double letter routes are farm to market roads that end at county roads or are former alignments of other highways.
Support. Missouri is the only state to extensively use lettering on its highway system. The 1952 Missouri 10-Year Highway Modernization and Expansion Program (the “Takeover Program”) upgraded 12,000 miles of county roads. The roads became known as supplemental routes. The program provided a state-maintained road within 2 miles of 95% of all rural units, such as farm homes, churches, schools, stores, etc. Missouri opted to use letters to label these routes to avoid confusion with the existing numbered routes.
903.7.12 Design of Route Sign Auxiliaries (MUTCD Section 2D.12)
Standard. All route sign auxiliaries shall match the color combination of the route sign that they supplement. If a route sign and its auxiliary signs are combined on a single sign with a green background, the auxiliary messages shall be white legends placed directly on the green background. Auxiliary signs shall not be mounted directly to a guide sign or other type of sign.
Option. A route sign and any auxiliary signs used with it may be combined on a single sign as a guide sign.
903.7.13 Junction Auxiliary Sign (M2-1) (MUTCD Section 2D.13)
Standard. The Junction (M2-1) auxiliary sign shall carry the abbreviated legend JCT and shall be mounted at the top of an assembly (see EPG 903.7.27) directly above the route sign, the sign for an alternative route (see EPG 903.7.16) that is part of the route designation, or the Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign where access is available only to one direction of the intersected route. The minimum size of the Junction auxiliary sign shall be 21 in. x 15 in. for compatibility with auxiliary signs carrying arrow symbols.
903.7.14 Cardinal Direction Auxiliary Signs (M3-1 through M3-4) (MUTCD Section 2D.15)
Guidance. Cardinal Direction auxiliary signs carrying the legend NORTH, EAST, SOUTH or WEST should be used to indicate the general direction of the entire route.
Standard. To improve the readability and recognition of the cardinal directions, the first letter of the cardinal direction words shall be ten percent larger, rounded up to the nearest whole number size.
If used, the Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign shall be mounted directly above a route sign or, if used, an auxiliary sign for an alternative route.
Guidance. Cardinal Directions shall not be used with a business route or Missouri Lettered route markers.
Support. Odd-numbered routes run north south; even-numbered routes east west.
903.7.15 Auxiliary Signs for Alternative Routes (M4 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.16)
Option. Auxiliary signs, carrying legends such as ALTERNATE, SPUR, or BUSINESS may be used to indicate an alternate route of the same number between two points on that route.
Standard. If used, the auxiliary signs for alternative routes shall be mounted directly above a route sign.
903.7.16 ALTERNATE Auxiliary Signs (M4-1) (MUTCD Section 2D.17)
Support. An alternate route starts at a point where it branches from the main numbered route, may pass through certain cities and towns and then connect back with the regular route some miles distant.
Option. The ALTERNATE (M4-1) auxiliary sign may be used to indicate an officially designated alternate routing of a numbered route between two points on that route.
Standard. If used, the ALTERNATE auxiliary sign shall be mounted directly above a route sign.
Guidance. The shorter (time or distance) or better-constructed route should retain the regular route number, and the longer or worse-constructed route should be designated the alternate route.
903.7.17 SPUR Auxiliary Sign (M4-1b)
Support. A spur is a highway that diverges from its primary parent highway to serve a specific area or connect to another highway
Option. The SPUR (M4-1b) auxiliary sign may be used to indicate a designated spur routing of a route.
Standard. If used, the SPUR auxiliary sign shall be mounted directly above a route sign. The SPUR auxiliary sign shall be used on Missouri numbered and letter routes. The SPUR auxiliary sign shall not be used on Interstates or U.S. routes.
903.7.18 BUSINESS Auxiliary Sign (M4-3) (MUTCD Section 2D.19)
Option. The BUSINESS (M4-3) auxiliary sign may be used to designate an alternate route that branches from a numbered route, passes through the business portion of a city and rejoins the numbered route beyond that area.
Standard. If used, the BUSINESS auxiliary sign shall be mounted directly above a route sign.
Cardinal Directions shall not be used with a business route.
903.7.19 TO Auxiliary Sign (M4-5) (MUTCD Section 2D.21)
Option. The TO (M4-5) auxiliary sign may be used to provide directional guidance to a particular road facility from other highways in the vicinity (see EPG 903.7.28).
Standard. If used, the TO auxiliary sign shall be mounted directly above a route sign or an auxiliary sign for an alternative route. If a Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign is also included in the assembly, the TO auxiliary sign shall be mounted directly above the Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign.
903.7.20 END Auxiliary Sign (M4-6) (MUTCD Section 2D.22)
Guidance. The END (M4-6) auxiliary sign should be used where the route being traveled ends, usually at a junction with another route. The END auxiliary sign is not to be used to indicate the end of a lettered route.
Standard. If used, the END auxiliary sign shall be mounted either directly above a route sign, above a sign for an alternative route or above a business route marker that is part of the designation of the route being terminated.
903.7.21 TEMPORARY Auxiliary Signs (M4-7) (MUTCD Section 2D.24)
Option. The TEMPORARY (M4-7) auxiliary sign may be used for an interim period to designate a section of highway that is not planned as a permanent part of a numbered route, but that connects completed portions of that route.
Standard. If used, the TEMPORARY auxiliary sign shall be mounted directly above the route sign, above a Cardinal Direction sign, or above a sign for an alternate route that is a part of the route designation. TEMPORARY auxiliary signs shall be promptly removed when the temporary route is abandoned.
903.7.22 Temporary Detour and Auxiliary Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.25)
Support. EPG 616.23 Traffic Control for Field Operations contains information regarding Temporary Detour and Auxiliary signs.
903.7.23 Advance Turn Arrow Auxiliary Signs (M5-1, M5-2, M5-3) (MUTCD Section 2D.26)
Standard. If used, the Advance Turn Arrow auxiliary sign shall be mounted directly below the route sign in Advance Route Turn assemblies and display a right or left arrow, the shaft of which is bent at a 90-degree angle (M5-1) or at a 45-degree angle (M5-2).
If used, the curved-stem Advance Turn Arrow auxiliary (M5-3) sign shall be used only on the approach to a circular intersection to depict a movement along the circulatory roadway around the central island and to the left, relative to the approach roadway and entry into the intersection.
Guidance. If the M5-3 sign is used, then this arrow type should also be used consistently on any regulatory lane-use signs, destination signs, and pavement markings for a particular destination or movement.
903.7.24 Lane Designation Auxiliary Signs (M5-4, M5-5, M5-6) (MUTCD Section 2D.27)
Option. A Lane Designation (M5-4, M5-5 or M5-6) auxiliary sign may be mounted directly below the route sign in an Advance Route Turn assembly on multi-lane roadways to allow road users to move into the appropriate lane prior to reaching the intersection or interchange.
Standard. If used, the Lane Designation auxiliary signs shall be used only where the designated lane is a mandatory movement lane and shall be located adjacent to the full-width portion of the mandatory movement lane. The Lane Designation auxiliary signs shall not be installed adjacent to a through lane in advance of a lane that is being added or along the taper for a lane that is being added.
903.7.25 Directional Arrow Auxiliary Signs (M6 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.28)
Standard. If used, the Directional Arrow auxiliary sign shall be mounted below the route sign and any other auxiliary signs in directional assemblies and display a single- or double-headed arrow pointing in the general direction that the route follows.
A directional arrow auxiliary sign that displays a double-headed arrow shall not be mounted in any directional assembly in advance of or at a circular intersection.
Guidance. The Straight Arrows (M6 Series) may be substituted for the Advance Turn arrows (M5-1 and M5-2) used near the “on” ramps of tight diamond interchanges to reduce the possibility of motorist confusion about which ramp to enter.
903.7.26 Route Sign Assemblies (MUTCD Section 2D.29)
Standard. A Route Sign assembly shall consist of a route sign and auxiliary signs that further identify the route and indicate the direction. Route Sign assemblies shall be installed on all approaches to numbered routes that intersect with other numbered routes.
Where two or more routes follow the same section of highway, the route signs for interstate, U.S., state and county routes shall be mounted in that order from the left in horizontal arrangements and from the top in vertical arrangements. Subject to this order of precedence, route signs for lower-numbered routes shall be placed at the left or top.
Within groups of assemblies, information for routes intersecting from the left shall be mounted at the left in horizontal arrangements and at the top or center of vertical arrangements. Similarly, information for routes intersecting from the right shall be at the right or bottom, and for straight-through routes at the center in horizontal arrangements or top in vertical arrangements.
Route Sign assemblies shall be mounted according to EPG 903.3.3 Mounting Height, with the lowest sign in the assembly at the height prescribed for single signs.
Guidance. Assemblies for two or more routes, or for different directions on the same route, should be mounted in groups on a common support.
Option. Route Sign assemblies may be installed on the approaches to numbered routes on unnumbered roads and streets that carry an appreciable amount of traffic destined for the numbered route.
If engineering judgment indicates that groups of assemblies that include overlapping routes or multiple turns might be confusing, route signs or auxiliary signs may be omitted or combined, provided that clear directions are given to road users.
Support. Refer to Typical Signing Applications for additional information.
These assemblies for independent use are Flat Sheet signs. For interstate shields, payment is the same, but these contain blue sheeting. For cardinal directions placed over the interstate shield, a note is placed on Form D-30 to indicate the number of cardinal directions which are interstate design, and which are the black on white type. This is also indicated for arrow signs placed below the interstate shield. For overlapping routes with an interstate and any other type of roadway containing the same cardinal direction, only one cardinal direction is required, and one arrow sign, with the interstate design being used, as indicated on typical signing plans for diamond interchanges and cloverleaf interchanges.
903.7.27 Junction Assembly (MUTCD Section 2D.30)
Standard. A Junction assembly shall consist of a Junction auxiliary sign and a route sign. The route sign shall carry the number, or letter, of the intersected or joined route.
The Junction assembly shall be installed in advance of every intersection where a state route is intersected or joined by another state route.
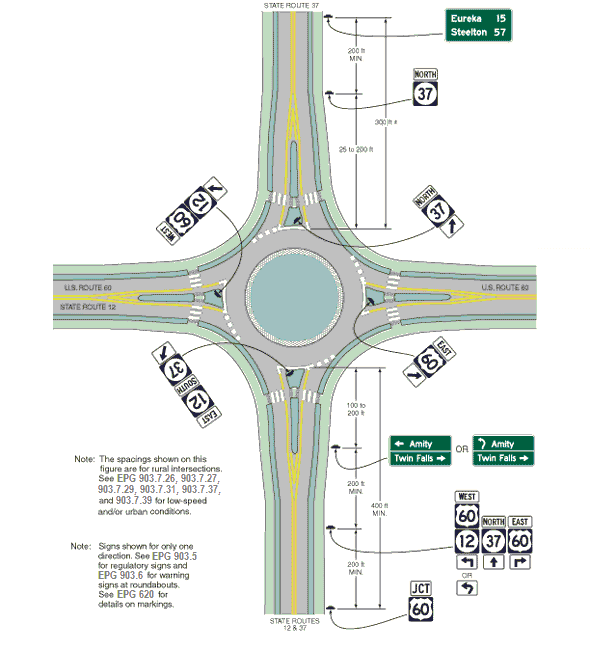
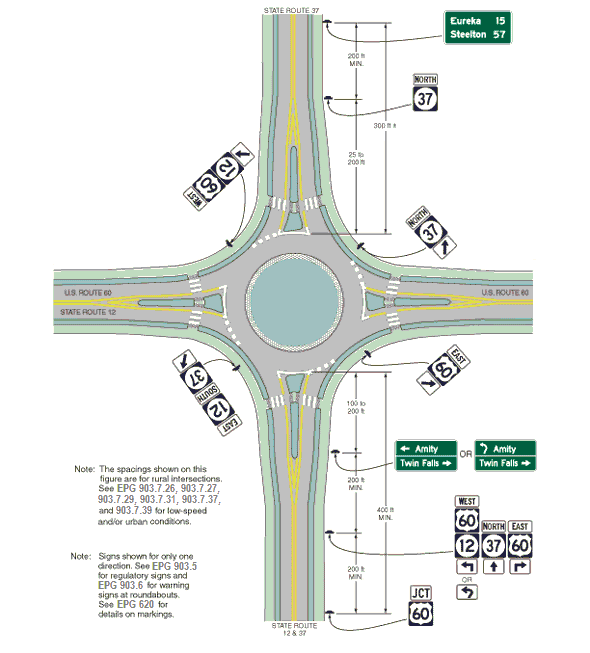
Guidance. In urban areas, the Junction assembly should be installed in the block preceding the intersection. In urban areas where speeds are low, the Junction assembly should not be installed more than 300 ft. in advance of the intersection.
In rural areas, the Junction assembly should be installed at least 400 ft. in advance of the intersection. In rural areas, the minimum distance between a Junction assembly and either a destination sign or an Advance Route Turn assembly should be 200 feet.
Where speeds are high, greater spacing should be used.
903.7.28 Advance Route Turn Assembly (MUTCD Section 2D.31)
Standard. An Advance Route Turn assembly shall consist of a route sign, an Advance Turn Arrow or word message auxiliary sign and a Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign, if needed. It shall be installed in advance of an intersection where a turn must be made to remain on the indicated route.
Option. The Advance Route Turn assembly may be used to supplement the required Junction assembly in advance of intersecting routes.
Guidance. Where a multiple-lane highway approaches an interchange or intersection with a numbered route, the Advance Route Turn assembly should be used to pre-position turning vehicles in the correct lanes from which to make their turn.
Option. Lane Designation auxiliary signs may be used in Advance Route Turn assemblies in place of the Advance Turn Arrow auxiliary signs where engineering judgment indicates that specific lane information associated with each route is needed and overhead signing is not practical and the designated lane is a mandatory movement lane. An assembly with the Lane Designation auxiliary signs may supplement or substitute for an assembly with Advance Turn Arrow auxiliary signs.
Standard. An assembly that includes an Advance Turn Arrow auxiliary sign shall not be placed so that an intersection is between it and the designated turn.
Guidance. Sufficient distance should be allowed between the assembly and any preceding intersection that could be mistaken for the indicated turn.
903.7.29 Directional Assembly (MUTCD Section 2D.32)
Standard. Directional assembly shall consist of a Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign, a route sign and a Directional Arrow auxiliary sign. The various uses of Directional assemblies shall be as provided in Items A through D:
- A. Turn movements (indicated in advance by an Advance Route Turn assembly) shall be marked by a Directional assembly with a route sign displaying the number of the turning route and a single-headed arrow pointing in the direction of the turn.
- B. The beginning of a route (indicated in advance by a Junction assembly) shall be marked by a Directional assembly with a route sign displaying the number of that route and a single-headed arrow pointing in the direction of the route.
- C. An intersected route (indicated in advance by a Junction assembly) on a crossroad where the route is designated on both legs shall be designated by:
- 1. Two Directional assemblies, each with a route sign displaying the number of the intersected route, a Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign, and a single-headed arrow pointing in the direction of movement on that route; or
- 2. A Directional assembly with a route sign displaying the number of the intersected route and a double-headed arrow, pointing at appropriate angles to the left, right or ahead.
- D. An intersected route (indicated in advance by a Junction assembly) on a side road or on a crossroad where the route is designated only on one of the legs shall be designated by a Directional assembly with a route sign displaying the number of the intersected route, a Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign and a single-headed arrow pointing in the direction of movement on that route.
Guidance. Straight-through movements should be indicated by a Directional assembly with a route sign displaying the number of the continuing route and a vertical arrow. A Directional assembly is not to be used for a straight-through movement in the absence of other assemblies indicating right or left turns, as the Confirming assembly sign beyond the intersection normally provides adequate guidance.
Directional assemblies should be located on the near right corner of the intersection. At major intersections and at Y or offset intersections, additional Directional assemblies should be installed on the far right or left corner to confirm the near-side assemblies. When the near-corner position is not practical for Directional assemblies, the far right corner should be the preferred alternative, with oversized signs, if necessary, for legibility. Where unusual conditions exist, the location of a Directional assembly should be determined by engineering judgment with the goal being to provide the best possible combination of view and safety.
Support. It is more important that guide signs be readable, and that the information and direction displayed thereon be readily understood, at the appropriate time and place than to be located with absolute uniformity. Refer to EPG 903.16 Typical Signing Applications for additional information.
903.7.30 Combination Lane-Use/Destination Overhead Guide Sign (MUTCD Section 2D.33)
Option. At complex intersection approaches involving multiple turn lanes and destinations, a Combination Lane-Use/Destination (D15-1) overhead guide sign that combines a lane-use regulatory sign with destination information such as a cardinal direction, a route number, a street name and/or a place name may be used.
Support. At such locations, the combined information on the D15-1 signs can be even more effective than separate lane-use and guide signs for conveying to unfamiliar drivers which lane or lanes to use for a particular destination.
Standard. The Combination Lane-Use/Destination (D15-1) overhead guide sign shall be used only where the designated lane is a mandatory movement lane. The D15-1 sign shall not be used for lanes with optional movements.
The D15-1 sign shall have a green background with a white border. The D15-1 sign shall be located approximately over the center of the lane to which it applies. If used on new projects, the lane-use sign shall be placed near the bottom of the sign and the destination information shall be placed near the top of the sign.
903.7.31 Confirming or Reassurance Assemblies (MUTCD Section 2D.34)
Standard. Confirming or Reassurance assemblies shall consist of a Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign and a route sign. Lettered routes, business routes, business loops and spurs do not receive Cardinal Direction auxiliary signs. Where the Confirming or Reassurance assembly is for an alternative route, the appropriate auxiliary sign for an alternative route shall also be included in the assembly.
Confirming or Reassurance assemblies shall be erected on the far side of all junctions to identify the route the driver is currently on. Confirming or Reassurance assemblies shall be used on the far side of major intersections in urban areas.
Guidance. A Confirming assembly should be placed 25 ft. to 200 ft. beyond the far shoulder or curb line of the intersected highway.
If used, Reassurance assemblies should be installed between intersections in urban areas as needed, and beyond the built-up area of any incorporated city or town.
Route signs for either confirming or reassurance purposes should be spaced at such intervals as necessary to keep road users informed of their routes.
A route sign should be placed 500 feet beyond the downstream end of interchange acceleration lanes confirming the route(s) the driver is entering onto.
Option. Additional confirmation assemblies may be used on the far side of minor intersections in heavy commercial or congested areas.
On freeways with emergency reference markers the confirmation route assembly may be omitted only if there is no overlapping route on that portion of the freeway, as the emergency reference marker serves as the confirmation.
903.7.32 Trailblazer Assembly (MUTCD Section 2D.35)
Support. Trailblazer assemblies provide directional guidance to a particular road facility from other highways in the vicinity. This guidance is accomplished by installing Trailblazer assemblies at strategic locations to indicate the direction to the nearest or most convenient point of access. The use of the word TO indicates that the road or street where the sign is posted is not a part of the indicated route and that a traveler is merely being directed progressively to the route.
Standard. A Trailblazer assembly shall consist of a TO auxiliary sign, a route sign for a numbered or named highway or an Auto Tour Route sign, and a single-headed Directional Arrow auxiliary sign pointing in the direction leading to the route. Where the Trailblazer assembly is for an alternative route, the appropriate auxiliary sign for an alternative route shall also be included in the assembly.
Option. A Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign may be used with a Trailblazer assembly.
Guidance. The TO auxiliary sign, Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign and Directional Arrow auxiliary sign should be of the standard size provided for auxiliary signs of their respective type. The route sign should be the size provided in EPG 903.7.11.
Trailblazer assemblies may be installed with other Route Sign assemblies, or alone, in the immediate vicinity of the designated facilities.
903.7.33 Destination and/or Distance Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.36)
Support. In addition to guidance by route numbers, it is desirable to supply the road user information concerning the destinations that can be reached by way of numbered or unnumbered routes. This is done by means of Destination and/or Distance signs.
States are not routinely listed as destinations in conjunction with the control city or destination. For example, when listing Des Moines on a guide sign, it is not necessary to list Iowa or the abbreviation IA. When ambiguity exits such as Kansas City, Missouri or Kansas City, Kansas, it becomes necessary to list the city with the state's proper abbreviation. Justification is required when using abbreviations of states or the entire state name on Destination and/or Distance Signs.
Option. Route shields and cardinal directions may be included on the Destination sign with the destinations and arrows.
Guidance. If Route shields and cardinal directions are included on a Destination sign, the height of the Route shields should be at least two times the height of the upper-case letters of the principal legend and not less than 18 inches, and the cardinal directions should be in all upper-case letters that are at least the minimum height specified for these signs.
Standard. Except where special interchange signing is prescribed, Destination and/or Distance Signs (D1-1, D2-1 and D1-1a Series) shall be white on green horizontal rectangle signs carrying the name of a city, town, village or other state route. The letters “MO” shall not be used, however, the letter “I” for interstate routes or “US” for United States routes will be shown. When state route is required, the legend ROUTE XX or its shield shall be used, regardless whether it is a numbered or lettered route. For signs with legends 8 inches or larger, Route Shields shall be used in lieu of text legend.
The order of destinations shall be ahead, left and then right. If there is more than one destination shown in the same direction, the name of the nearest destination shall appear above the names of any destinations that are farther away.
Destinations shall not include traffic generators such as universities, stadiums, amusement parks or other publicly or privately owned attractions.
Guidance. No more than three destinations should be used on a Destination and/or Distance Sign (D1-1, D2-1 and D1-1a Series).
Adequate separation should be made between any destinations or group of destinations in one direction and those in other directions by suitable design of the arrow, spacing of lines of legend, heavy lines entirely across the panel or separate panels.
Destinations should appear on all subsequent Destination and/or Distance Signs (D1-1, D2-1, and D1-1a Series) for continuity until the corporate limits of the destination are reached.
Option. Unincorporated communities may be used on Destination and/or Distance Signs (D1-1, D2-1 and D1-1a Series) at junctions of state routes where it is more appropriate than using incorporated communities if that destination meets the qualifications of EPG 903.9.9.
Standard. On DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1 Series) and DISTANCE AND DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1a Series), an arrow pointing to the right shall be at the extreme right of the sign, and an arrow pointing left or up shall be at the extreme left.
Guidance. Arrows used on DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1 Series) and DISTANCE AND DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1a Series) for conventional routes should be limited to left, thru and right arrows. Unless a sloping arrow conveys a clearer indication of the direction to be followed, the directional arrows should be horizontal or vertical.
When used in high-speed areas, DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1 Series) and DISTANCE AND DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1a Series) should be located 200 ft. or more in advance of the intersection and following any Junction or Advance Route Turn assemblies that may be required.
Option. In urban areas, shorter advance distances may be used.
Because the DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1 Series) and DISTANCE AND DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1a Series) are of lesser importance than the Junction, Advance Route Turn or Directional assemblies, the DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1 Series) and DISTANCE AND DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1a Series) may be eliminated when sign spacing is critical.
Standard. For DISTANCE AND DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1a Series) and DISTANCE SIGNS (D2-1 Series), mileages to towns and cities shall be based on the control point of that town or city. Control points are usually a major intersection with another state route, near the business district of that town or city. In no case should the mileage shown on the DISTANCE AND DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1a Series) or DISTANCE SIGNS (D2-1 Series) at an intersection exit be different from that shown for the same destination on any other leg of the approach to/from said intersection.
Terminal points for use in determining distances for DISTANCE AND DESTINATION SIGNS (D1-1a Series) and DISTANCE SIGNS (D2-1 Series) to more important towns and cities shall be revised and furnished by the State Highway Safety and Traffic Engineer, upon request.
The selection of destinations on a Distance sign shall be determined by the following rules:
- A. The first or top line shall identify the next interchange or community along the route;
- B. If used, the second or middle line should list the next control point on the route; and
- C. The third or bottom line shall identify the next control city on the route.
Guidance. Distances should be rounded to the nearest whole mile and the distances should be to the actual destination, not the ramp exit gore, city limits, or intersection.
Distance signs may have one line or a maximum of three lines.
Distances may be a number of miles from the route terminus.
On two-lane roads where the distance between intersections of numbered routes exceeds 10 miles, additional Distance signs should be placed after intersections with lettered routes so that the spacing between Distance signs does not exceed 10 miles.
The control city should remain the same on all successive Distance signs throughout the length of the route until that city is reached.
Option. If more than one distant point may properly be designated (e.g. where the route divides at some distance ahead to serve two destinations of similar importance) and if these two destinations cannot appear on the same sign, the two names may be alternated on successive signs.
On a route extending into another state, destinations in the adjacent state may be shown.
| MoDOT routes approved for distance signing |
| Control Points - Distance Signing |
Support. Control cities are defined for the interstate system in the AASHTO List of Control Cities for Use in Guide Signs on Interstate Highways and Table 903.8.11, Interstate Sign Control Cities. Control cities on other systems are determined as the next community located where the route intersects with a U.S. numbered route. A list of routes eligible for distance signing and the appropriate control points is available.
Guidance. The destination shown for each direction should ordinarily be the next county seat or the next principal city, rather than a more distant destination. In the case of overlapping routes, there should be shown only one destination in each direction for each route.
903.7.34 Destination Signs (D1 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.37)
Standard. Destination (D1-1 through D1-3) signs shall be a horizontal rectangle displaying the name of a city, town or village and a directional arrow indicating the direction to the destination. Destination (D1 Series) signs shall not indicate distance to the destination.
Destination signs shall be provided at the junctions of all interstate, U.S. and state routes except where it is deemed not appropriate or routes that have no destination to be listed. Locations for which Destination signs might not be appropriate are business routes, loops, alternate routes or locations signed in EPG 903.7.40, Destination and Distance Signs (D1-1a Series).
Destination signs shall be installed along crossroads within the limits of an interchange. At intersections where a Distance (D2 Series) is provided after the turn, a Destination sign shall be installed on the approach to the intersection.
Guidance. If several individual name signs are assembled into a group, all signs in the assembly should be of the same horizontal width.
In the case where no communities exist, numbered routes should be provided on the Destination (D1-1 Series) signs.
903.7.35 Destination Signs at Circular Intersections (MUTCD Section 2D.38)
Standard. Destination signs that are used at circular intersections shall comply with the provisions of EPG 903.7.34.
Option. Exit destination (D1-1d, D1-1e) signs with diagonal upward-pointing arrows or Directional assemblies may be used to designate a particular exit from a circular intersection.
Exit destination (D1-2d, D1-3d) signs with curved-stem arrows may be used on approaches to circular intersections to represent the left-turn movements.
Curved-stem arrows on circular intersection destination signs may point in diagonal directions to depict the location of an exit relative to the approach roadway and entry into the intersection.
Guidance. If curved-stem arrows are used on destination signs, then this arrow type should also be used consistently on any regulatory lane-use signs, Directional assemblies, and pavement markings for a particular destination or movement.
Support. Figs. 903.7.35.1 and 903.7.35.2 illustrate two examples of guide signing for circular intersections.
EPG 903.5 contains information regarding regulatory signs at circular intersections and EPG 903.6 contains information regarding warning signs at circular intersections.
Standard. Diagrammatic guide signs for circular intersections shall not be used.
903.7.36 Destination Signs at Jughandles (MUTCD Section 2D.39)
Standard. Destination signs that are used at jughandles shall comply with the provisions of EPG 903.7.34.
903.7.37 Location of Destination Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.40)
Support. Refer to EPG 903.16 Typical Signing Applications for typical placements of Destination signs.
903.7.38 Distance Signs (D2 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.41)
Standard. If used, the Distance (D2-1 through D2-3) signs shall be a horizontal rectangle of a size appropriate for the required legend, carrying the names of no more than three cities, towns, or junctions.
The Distance numerals shall be placed to the right of the destination names.
Distance signs shall display the distance (to the nearest mile) to the destination in the forward direction. Distance signs shall not include arrows.
Guidance. Distance (D2 Series) signs should be erected on Interstate, U.S. numbered, and Missouri numbered routes only and shall be erected for example:
- A. When leaving an incorporated area;
- B. Following an on ramp at an interchange; and
- C. Following an intersection with another numbered route.
Distance signs should not be erected in urban areas, except following an interchange.
903.7.39 Location of Distance Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.42)
Guidance. If used, Distance signs should be installed on important routes leaving municipalities and just beyond intersections of numbered routes in rural areas. If used, they should be placed just outside the municipal limits or at the edge of the built-up area if it extends beyond the limits.
Where overlapping routes separate a short distance from the municipal limits, the Distance signs at the municipal limits should be omitted. The Distance sign should be installed approximately 300 ft. beyond the separation of the two routes.
Where, just outside of an incorporated municipality, two routes are concurrent and continue concurrently to the next incorporated municipality, the top name on the Distance sign should be that of the place where the routes separate; the bottom name should be that of the city to which the greater part of the through traffic is destined.
Support. EPG 903.16 Typical Signing Applications shows typical placements of Distance signs.
903.7.40 Destination and Distance Signs (D1a Series)
Standard. Destination and Distance (D1-1a through D1-3a) signs shall display a directional arrow and distance to the destination.
Destination and Distance (D1a Series) signs shall not be installed within the limits of an interchange, except at the ramp terminal.
At an intersection, where a Distance (D2 Series) sign is not provided leaving the intersection or at the end of the ramp terminal, a Destination and Distance sign shall be used in advance of the intersection.
An arrow pointing to the right shall be at the extreme right of the sign, and an arrow pointing left or up shall be at the extreme left. The distance figures shall be placed to the right of the destination names.
903.7.41 Street Name Signs (D3-1 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.43)
Standard. The Street Name sign shall be retroreflective or illuminated to show the same shape and similar color both day and night. The color of the legend and border shall contrast with the background color of the sign.
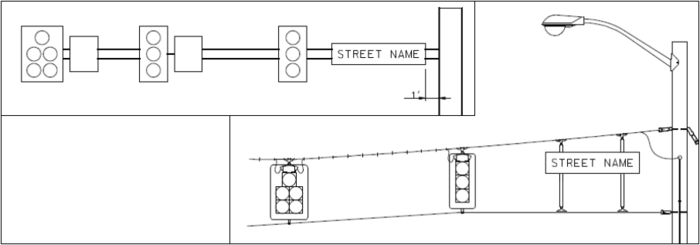
MoDOT shall only install Street Name signs at signalized intersection approaches that have been officially named by the local jurisdiction. Street Name signs are not installed for any approach to fire stations, commercial entrances, schools, or an entrance to a freeway or expressway-type highway. The Street Name signs shall be mounted on a mast arm and on span wire signals between the carrier and tether wires and shall be mounted a maximum of 12 inches from the center of the upright support. This distance may be increased on span wire signals if the support isn’t adjacent to the roadway (see Fig. 903.7.41).
Requests for a Street Name sign from individuals shall not be considered. The Street Names sign erected by others shall be a minimum of 7 ft. above the roadway surface and a minimum of 2 ft. beyond all shoulder points. All locations shall be field checked before installation approval is granted.
One-line Street Name (D3-1) signs shall be used when mounting onto either a signal mast arm or between the carrier and tether wires on span wire signals. This sign shall be 18 inches tall by variable length, not to exceed 8 feet.
Two-line Street Name (D3-1b) signs shall be mounted onto either a signal mast arm or between tether wires on span wire signals. This sign shall be 18 inches tall by variable length, not to exceed 8 feet.
D3-1 signs mounted on vertical signal posts shall be 12 inches tall by variable length, not to exceed 4 feet.
If a Street Name sign is installed above a STOP sign, it shall be located with a vertical clearance between 1 inch and 4 inches measured from the bottom of the Street Name sign to the top of the STOP sign. The Street Name sign shall be mounted independently of the STOP sign and the installation shall not interfere with the maintenance of the STOP sign. Only one Street Name sign shall be allowed for a side street and shall be mounted above the STOP sign. MoDOT shall maintain the STOP sign and post. Maintenance of the Street Name sign shall be the responsibility of the local political subdivision. It is not MoDOT’s intention to upgrade existing STOP sign posts to allow the addition of a Street Name sign. Attachments to our existing STOP sign post shall be by bracket, flat stock, channel “U” posts, or other methods approved by MoDOT. The maximum width of a Street Name sign placed over a MoDOT STOP sign shall not exceed the width of the STOP sign.
When a Street Name sign, erected by others, is installed on a separate post, maintenance of the Street Name sign and post shall be the responsibility of the political subdivision.
MoDOT shall not participate in the establishment, procurement or installation of any local route markers.
MoDOT's route numbering system shall be considered when developing the local route numbering system in order to preclude the possibility of the route number of the local system intersecting the same number of the state system.
The local route signing shall be limited to one installation per direction for an intersection.
If D3-1 series signs are being used, then they shall be installed according to the Street Name signing for non-signalized intersections.
All locations should be field checked before installation to ensure the sign causes no reduction in sight distance.
Option. Any political subdivision may erect, furnish and maintain a Street Name sign of the same type as the D3-1 series on state right of way at non-signalized intersections. Conventional abbreviations (refer to Abbreviations Used on Traffic Control Devices) may be used except for the street name itself.
A symbol or letter designation may be used on a Street Name sign to identify the governmental jurisdiction, area of jurisdiction or other government-approved institution.
Street Name signs may be either the street name (surname) or route identification and may display block numbers or a logo to compliment the design of the signs used by the community a state route passes through. Because there are size limitations for Street Name signs, these features will be omitted if the space is required for sign legend.
Standard. If a symbol or letter designation is used, the height and width of the symbol or letter designation shall not exceed the letter height of the sign, see Table 903.7.41.
Table 903.7.41 Recommended Minimum Letter Heights on Street Name Signs
| Type of Mounting | Type of Street or Highway | Speed Limit | Recommended Minimum Letter Height | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Upper-Case (in.) | Lower-Case (in.) | |||
| Overhead | All types | All speed limits | 12 | 9 |
| Post-mounted | Multi-lane | More than 40 mph | 8 | 6 |
| Post-mounted | Multi-lane | 40 mph or less | 6 | 4.5 |
| Post-mounted | 2-lane | All speed limits | 6* | 4.5* |
| * On local two-lane streets with speed limits of 25 mph or less, 4 in. initial upper-case letters with 3 in. lower-case letters may be used. | ||||
Guidance. The symbol or letter designation should be positioned to the left of the street name.
Standard. Alternative background colors shall not be used for Advance Street Name (D3-2) signs.
MoDOT’s standard street name color is white legend on a green background. If a local jurisdiction requests an alternate color for the street name signs in their jurisdiction, the only acceptable alternative background colors for Street Name (D3-1 or D3-1b) signs shall be blue, brown, or white. Regardless of whether green, blue, or brown is used as the background color for Street Name signs, the legend and border shall be white. For Street Name signs that use a white background, the legend and border shall be black. The local subdivision shall provide the entire route with the same colors.
If an alternative background color is requested by a local jurisdiction, that jurisdiction will be responsible for the cost of upgrading the street name signs to the new color if the MoDOT signs are replaced prematurely.
Guidance. Encourage the local subdivision to use route markers like either our Street Name, D3-1 sign or a local route shield similar to that shown in the MUTCD as sign number M1-5.
Street Name signs should have a white legend on a green background. A border should be the same color as the legend.
In business districts and on principal arterials, Street Name signs should be placed at least on diagonally opposite corners. In residential areas, at least one Street Name sign should be mounted at each intersection. Signs naming both streets should be installed at each intersection and should be mounted with their faces parallel to the streets they name.
On two-line type Street Name signs arrows should be used to indicate which side of the street the name applies.
The width of a Street Name sign mounted above a STOP sign is not to be greater than the width of the STOP sign it is mounted over. Route marking shield signs are not to be installed above our STOP sign.
The Street Name sign should be mounted with its face parallel to the street it is naming. If the Stop sign has ONE WAY signs mounted above it, such as on expressways, the Street Name sign should be installed on a separate post.
When a Street Name sign, erected by others, is installed on a separate post, the sign should be located near the STOP sign and not block the face of the STOP sign. If the Street Name sign is being installed at a location where there is no STOP sign, it should be located on the far right-hand side of the intersection for traffic on the major street. Any Street Name sign should be mounted with its face parallel to the street it is naming.
In areas where we have narrow right of way, consideration should be given to placing the Street Name sign at the right of way if sight distance permits.
Option. To optimize visibility, Street Name signs may be mounted overhead. Street Name signs may also be placed above a regulatory or STOP or YIELD sign.
At intersection crossroads where the same road has two different street names for each direction of travel, both street names may be shown on the same sign along with directional arrows.
If local route shield type signs are being used, the signs may be installed in one of the following ways: at the right of way line facing either parallel or perpendicular to the highway; at the intersection near, but not to block, the stop sign; or in advance of the intersection with the appropriate horizontal arrow of the same width as the shield.
Support. Information regarding the use of street names on supplemental plaques for use with intersection-related warning signs is contained in EPG 903.6.43.
In those cases where the local jurisdiction has not designated a street name to the state route, it is acceptable to use the route number or letter on the Street Name signs.
903.7.42 Advance Street Name Signs (D3-2 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.44)
Support. Advance Street Name (D3-2 Series) signs identify an upcoming intersection. Although this is often the next intersection, it could also be several intersections away in cases where the next signalized intersection is referenced.
Standard. Advance Street Name (D3-2 Series) signs, if used, shall supplement rather than be used instead of the Street Name (D3-1 series) signs at the intersection.
Option. Advance Street Name (D3-2 Series) signs may be installed in advance of unsignalized intersections within a corridor of signalized intersections, which have Advance Street Name signs. The purpose should provide road users with advance information to identify the name(s) of the next intersecting street to prepare for crossing traffic and to facilitate timely deceleration and/or lane changing in preparation for a turn.
Special consideration may be given to isolated unsignalized intersections where it can be established that safety problems exist and installation of this type of signing would be beneficial.
Guidance. On arterial highways in rural areas, Advance Street Name signs should be used in advance of all signalized intersections and in advance of all intersections with exclusive turn lanes.
In urban areas, Advance Street Name signs should be used in advance of all signalized intersections on divided highways, major arterial streets or other routes as determined by the district except where signalized intersections are so closely spaced that advance placement of the signs is impractical.
If there is concern that the action message for Advance Street Name signs for unsignalized intersections could be misleading due to other entrances in the area or the sight distance to the intersection is limited, then the action message should be the distance shown to the nearest 100 ft.
Advance Street Name sign placement should be one-half or one-quarter mile in advance of the signal or intersection. In the event of closely spaced signals, this sign should be located immediately beyond the adjacent signalized or unsignalized intersection.
Standard. If used, Advance Street Name signs shall have a white legend and border on a green background.
If used for signalized intersections, Advance Street Name signs shall provide the name(s) of the intersecting street(s) on the top line(s) of the legend and messages such as the abbreviation for junction (JCT) and a route shield if the cross street is a state highway and (or) NEXT SIGNAL.
If used for unsignalized intersections, Advance Street Name signs shall provide the name(s) of the intersecting street(s) on the top lines(s) of the legend and messages such as the abbreviation for junction (JCT) and a route shield if the cross street is a state highway and an action message. The recommended action message for these signs is NEXT INTERSECTION or LEFT or RIGHT. When the Advance Street Name sign is provided for at the junction of a state highway, the Advance Street Name sign shall replace the existing junction assembly.
The installation of an Advance Street Name sign for an unsignalized intersection shall be a supplement to any Street Name signing provided by others.
Pictographs shall not be displayed on Advance Street Name signs.
Option. Directional arrow(s) may be placed to the right or left of the street name or message such as NEXT SIGNAL, as appropriate, rather than on the bottom line of the legend. Curved-stem arrows may be used on Advance Street Name signs on approaches to circular intersections.
For intersecting crossroads where the same road has a different street name for each direction of travel, the different street names may be displayed on the same Advance Street Name sign along with directional arrows.
In advance of two closely spaced intersections where it is not practical to install separate Advance Street Name signs, the Advance Street Name sign may include the street names for both intersections along with appropriate supplemental legends for both street names, such as NEXT INTERSECTION, 2ND INTERSECTION, NEXT LEFT and NEXT RIGHT, or directional arrows.
Guidance. If two street names are used on the Advance Street Name sign, the street names should be displayed in the following order:
A. For a single intersection where the same road has a different street name for each direction of travel, the name of the street to the left should be displayed above the name of the street to the right; or
B. For two closely-spaced intersections, the name of the first street encountered should be displayed above the name of the second street encountered, and the arrow associated with the second street encountered should be an advance arrow, such as the arrow shown on the W16-6P arrow plaque.
Option. An Advance Street Name (W16-8P or W16-8aP) plaque with black legend on a fluorescent yellow background, installed supplemental to an Intersection (W2 series) or Advance Traffic Control (W3 series) warning sign may be used instead of an Advance Street Name guide sign only if the advance warning sign is justified.
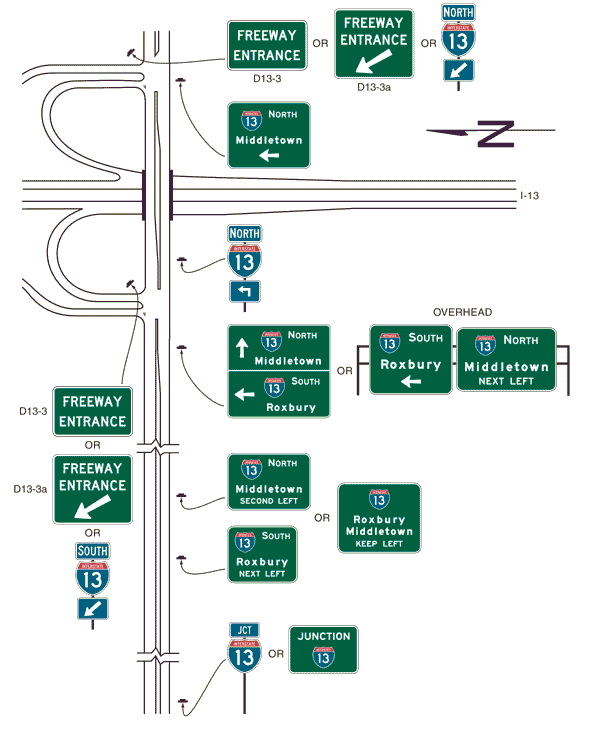
903.7.43 Signing on Conventional Roads on Approaches to Interchanges (MUTCD Section 2D.45)
Support. Because there are a number of different ramp configurations that are commonly used at interchanges with conventional roads, drivers on the conventional road cannot reliably predict whether they will be required to turn left or right in order to enter the correct ramp to access the freeway or expressway in the desired direction of travel. Consistently applied signing for conventional road approaches to freeway or expressway interchanges is highly desirable.
Standard. On multi-lane conventional roads approaching an interchange, guide signs shall be provided to identify which direction of turn is to be made and/or which specific lane to use for ramp access to each direction of the freeway or expressway.
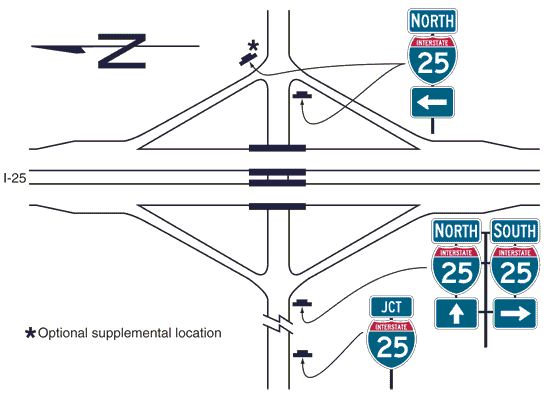
Guidance. The signing of conventional roads with one lane of traffic approaching an interchange should consist of a sequence containing the following signs (see Fig. 903.7.43.1):
- A. Junction Assembly
- B. Destination sign
- C. Directional Assembly or Entrance Direction sign for the first ramp
- D. Advance Route Turn Assembly or Advance Entrance Direction sign with an advance turn arrow
- E. Directional Assembly or Entrance Direction sign for the second ramp
Standard. If used, the Entrance Direction sign shall consist of a white legend and border on a green background. It shall contain the freeway or expressway route shield(s), cardinal direction, and directional arrow(s).
Option. The Entrance Direction sign may contain a destination(s) and/or an action message such as NEXT RIGHT. The following sequence of signs may be used (see Fig. 903.7.43.2):
- A. Junction Assembly
- B. Directional Assembly for the first ramp
- C. Directional Assembly of the second ramp
Guidance. On multi-lane conventional roads approaching an interchange, the sign sequence should contain the following signs (see Figs. 903.7.43.3 through 903.7.43.5):
- A. Junction Assembly
- B. Advance Entrance Direction sign(s) for both directions, if applicable, of travel on the freeway or expressway
- C. Entrance Direction sign for first ramp
- D. Advance Turn Assembly
- E. Entrance Direction sign for the second ramp
Support. Advance Entrance Direction signs are used to direct road users to the appropriate lane(s).
Standard. The Advance Entrance Direction sign shall consist of a white legend and border on a green background. It shall contain the freeway or expressway route shield(s) and cardinal direction(s).
Option. The Advance Entrance Direction sign may have destinations, directional arrows, and/or an action message such as KEEP LEFT, NEXT LEFT or SECOND RIGHT. Signs in this sequence may be mounted overhead to improve visibility as shown in Figs. 903.7.43.3 through 903.7.43.5.
Support. A post-mounted Advance Entrance Direction diagrammatic guide sign (see Fig. 903.7.43.6), within the sequence of approach guide signing, might be helpful in depicting the location of a freeway or expressway entrance ramp that is in close proximity to an intervening intersection on the same side of the approach roadway and where signing for only the ramp might cause confusion to road users.
Standard. If used, the post-mounted Advance Entrance Direction diagrammatic guide sign displays only the two successive turns from the same side of the roadway, one of which shall be the entrance ramp. The post-mounted Advance Entrance Direction sign shall depict only the successive turns and shall not depict lane use with lane lines, multiple arrow shafts for the approach roadway, action messages, or other representations.
903.7.44 Lake Road Signs (M1-15)
Standard. Lake Road signs have been discontinued. MoDOT shall no longer provide Lake Road signs. Existing Lake Road signs shall be left in place until they reach the end of their service life.
Guidance. The districts should give advanced notice to the local jurisdictions making them aware that MoDOT will no longer be providing Lake Road signs so that the local jurisdiction can fabricate and install street signs in accordance with MUTCD standards.
903.7.45 MoDOT Maintenance Signs (M19-1, M19-2)
Standard. The MAINTENANCE ENDS (M19-2) sign shall be erected at the end of MoDOT maintenance on all marked highways except at a state line.
The MAINTENANCE BEGINS (M19-1) sign has been discontinued for normal use. MoDOT shall no longer provide MAINTENANCE BEGINS signs. Existing MAINTENANCE BEGINS signs shall be left in place until they reach the end of their service life.
Option. When state maintenance begins and ends at multiple locations along a route’s length as it enters and exits various municipalities, a MAINTENANCE BEGINS (M19-1) sign may be used to mark the boundaries of MoDOT maintenance responsibilities.
Guidance. The MAINTENANCE ENDS signs are not to be placed to mark the maintenance responsibilities for crossroads, such as within interchange limits unless there is a specific problem.
903.7.46 Parking Area Guide Sign (D4-1) (MUTCD Section 2D.47)
Option. The Parking Area (D4-1) guide sign may be used to show the direction to a nearby public parking area or parking facility. The sign may also be used in all MoDOT commuter parking lots.
Standard. The area shall be owned or operated by a public agency in order to be signed. If used, the Parking Area guide sign shall be a horizontal rectangle. The legend and border shall be green on a retroreflectorized white background.
The COMMUTER (D4-1P) plaque shall be mounted above the Parking Area sign at commuter parking lots. If used, the sign shall be a horizontal rectangle. The legend and border shall be green on a retroreflectorized white background.
COMMUTER PARKING (D4-1a) signs shall be utilized in each commuter parking area mounted back-to-back. One sign shall face the Interstate and the other will face the parking lot such that the maximum number of motorists on either side of the assembly can read the legend.
In addition, Commuter Parking Lot Restriction signs shall be erected at or near each entrance to the commuter parking lot.
Guidance. If used, the Parking Area (D4-1) guide sign should be installed as 1st order signing to the parking facility and where it can advise drivers of a place to park. The sign should not to be used more than four blocks from the parking area.
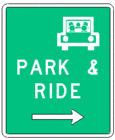
903.7.47 PARK - RIDE Sign (D4-2) (MUTCD Section 2D.48)
Option. PARK - RIDE (D4-2) signs may be used to direct road users to park - ride facilities.
The PARK - RIDE signs may be used in lieu of the Parking sign when a public transit stop is located within the commuter parking lot.
Standard. The signs shall contain the word message PARK - RIDE and direction information (arrow or word message).
Option. PARK - RIDE signs may contain the local transit pictograph and/or carpool symbol on the sign.
Standard. If used, the local transit pictograph and/or carpool symbol shall be located in the top part of the sign above the message PARK - RIDE. In no case shall the vertical dimension of the local transit pictograph and/or carpool symbol exceed 18 inches.
Guidance. If the function of the parking facility is to provide parking for persons using public transportation, the local transit pictograph should be used on the guide sign. If the function of the parking facility is to serve carpool riders, the carpool symbol should be used on the guide sign. If the parking facility serves both functions, both the pictograph and carpool symbol should be used. If used, the public transit pictograph should be of the same design as the local transit authority, however, the local transit authority name should not be a part of this sign.
The existing COMMUTER (D4-1P) plaque should be mounted below this sign.
Standard. These signs shall have a retroreflective white legend and border on a rectangular green background. The carpool symbol shall be as shown for the D4-2 sign. The color of the local transit pictograph shall be selected by the local transit authority.
Option. To increase the target value and contrast of the local transit pictograph, and to allow the local transit pictograph to retain its distinctive color and shape, the pictograph may be included within a white border or placed on a white background.
903.7.48 Weigh Station Signing (D8 Series) (MUTCD Section 2D.49)
Support. The general concept for Weigh Station signing is similar to Rest Area signing because in both cases traffic using either area remains within the right of way.
Standard. Traffic control signs in weigh stations shall be maintained by MoDOT. The standard installation for Weigh Station signing shall include three basic signs:
- A. Advance sign (D8-1);
- B. Exit Direction sign (D8-2a); and
- C. Exit Gore sign (D8-3).
See Standard Plan 903.04 for further information.
The OFFICIAL WEIGH STATION (F3-1) sign shall be used to identify all official weigh stations. If the weigh station uses a prepass system a PREPASS SITE ALL TRUCKS RIGHT LANE sign shall be used.
Option. If the weigh station uses a preclearance system an advanced preclearance sign may be installed by the vendor of the system based on their contract.
Support. Example locations of these signs are shown in Figure 903.7.48.
Guidance. The Exit Direction sign (D8-2a) or the Advance sign (D8-1) should display, either within the sign border or on a supplemental plaque of sign panel, the changeable message OPEN or CLOSED.
The Official Weigh Station sign should be erected over the platform scales so that the lower edge of the sign will be 16 ft. above the platform.
Option. The Official Weigh Station sign may also be post-mounted.
903.7.49 Community Wayfinding Signs (MUTCD Section 2D.50)
| Useful Information for Local Agencies |
| Key Wayfinding Requirements |
| Includes information about sign posts, the number and placement of wayfinding destinations, the use of arrows, colors, legends, fabrication and retroreflectivity. |
Support. Community wayfinding guide signs are part of a coordinated and continuous system of signs that direct tourists and other road users to key civic, cultural, visitor, and recreational attractions and other destinations within a city or a local urbanized or downtown area.
Community wayfinding guide signs are a type of destination guide sign for conventional roads with a common color and/or identification enhancement marker for destinations within an overall wayfinding guide sign plan for an area.
Fig. 903.7.49.1 illustrates various examples of the design and application of community wayfinding guide signs.
Standard. The use of community wayfinding guide signs shall be limited to conventional roads. Community wayfinding guide signs shall not be installed on freeway or expressway mainlines or ramps. Direction to community wayfinding districts from a freeway or expressway shall be limited to the use of a Supplemental Guide sign on the mainline and a Destination sign on the ramp to direct road users to community wayfinding. A community wayfinding program shall have a minimum of three well defined districts before freeway/expressway signing will be permitted. A well-defined district shall represent a region or area with multiple sites or destinations within it. See Figure 903.7.49.2 and Figure 903.7.49.3. The individual wayfinding destinations shall not be displayed on the Supplemental Guide and Destination signs except where the destinations are in accordance with this policy.
Community wayfinding guide signs shall not be used to provide direction to primary destinations or highway routes or streets. Destination or other guide signs shall be used for this purpose as described elsewhere in the EPG and shall have priority over any community wayfinding sign in placement, prominence and conspicuity.
Because regulatory, warning and other guide signs have a higher priority, community wayfinding guide signs shall not be installed where adequate spacing cannot be provided between the community wayfinding guide sign and other higher priority signs. Community wayfinding guide signs shall not be installed in a position where they would obscure the road users’ view of other traffic control devices.
Community wayfinding guide signs shall not be mounted overhead. Community wayfinding guide signs include boundary markers, welcome to messages or the simple display of a city name on a structure or sign. Refer to EPG 903.4 Overhead Sign Mounting.
Guidance. If used, a community wayfinding guide sign system should be established on a local municipal or equivalent jurisdictional level or for an urbanized area of adjoining municipalities or equivalent that form an identifiable geographic entity that is conducive to a cohesive and continuous system of signs. Community wayfinding guide signs should not be used on a regional or statewide basis where infrequent or sparse placement does not contribute to a continuous or coordinated system of signing that is readily identifiable as such to the road user. In such cases, Destination or other guide signs detailed elsewhere in the EPG should be used to direct road users to an identifiable area in which the type of eligible destination is located.
Support. The specific provisions of this article regarding the design of community wayfinding sign legends apply to vehicular community wayfinding signs and do not apply to those signs that are intended only to provide information or direction to pedestrians or other users of a sidewalk or roadside area.
Guidance. Because pedestrian wayfinding signs typically use smaller legends that are inadequately sized for viewing by vehicular traffic and because they can provide direction to pedestrians that might conflict with that appropriate for vehicular traffic, wayfinding signs designed for and intended to provide direction to pedestrians or other users of a sidewalk or other roadside area should be located to minimize their conspicuity to vehicular traffic. Such signs should be located as far as practical from the street, such as at the far edge of the sidewalk. Where locating such signs farther from the roadway is not practical, the pedestrian wayfinding signs should have their conspicuity to vehicular traffic minimized by employing one or a combination of the following methods:
- A. Locating signs away from intersections where high-priority traffic control devices are present.
- B. Facing the pedestrian message toward the sidewalk and away from the street.
- C. Cantilevering the sign over the sidewalk if the pedestrian wayfinding sign is mounted at a height consistent with vehicular traffic signs, removing the pedestrian wayfinding signs from the line of sight in a sequence of vehicular signs.
To further minimize their conspicuity to vehicular traffic during nighttime conditions, pedestrian wayfinding signs should not be retroreflective.
Support. Color coding is sometimes used on community wayfinding guide signs to help road users distinguish between multiple potentially confusing traffic generator destinations located in different neighborhoods or subareas within a community or area.
Option. At the boundaries of the geographical area within which community wayfinding guide signing is used, an informational guide sign may be posted to inform road users about the presence of wayfinding signing and to identify the meanings of the various color codes or pictographs that are being used.
Standard. These informational guide signs shall have a white legend and border on a green background and shall have a design similar to that illustrated in Fig. 903.7.49.3 and shall be consistent with the basic design principles for guide signs. These informational guide signs shall not be installed on freeway or expressway mainlines or ramps.
The color coding or a pictograph of the identification enhancement markers of the community wayfinding guide signing system shall be included on the informational guide sign posted at the boundary of the community wayfinding guide signing area. The color coding or pictographs shall apply to a specific, identifiable neighborhood or geographical subarea within the overall area covered by the community wayfinding guide signing. Color coding or pictographs shall not be used to distinguish between different types of destinations that are within the same designated neighborhood or subarea. The color coding shall be accomplished by the use of different colored square or rectangular panels on the face of the informational guide sign, each positioned to the left of the neighborhood or named geographic area to which the color-coding panel applies. The height of the colored square or rectangular panels shall not exceed two times the height of the upper-case letters of the principal legend on the sign.
Option. The different colored square or rectangular panels may include either a black or a white (whichever provides the better contrast with the color of the panel) letter, numeral, or other appropriate designation to identify the destination.
Except for the informational guide sign posted at the boundary of the wayfinding guide sign area, community wayfinding guide signs may use background colors other than green in order to provide a color identification for the wayfinding destinations by geographical area within the overall wayfinding guide signing system. Color-coded community wayfinding guide signs may be used with or without the boundary informational guide sign displaying corresponding color-coding panels. Except as provided below, in addition to the colors that are approved in this article for use on official traffic control signs, other background colors may also be used for the color coding of community wayfinding guide signs.
Standard. The standard colors of red, orange, yellow, purple, or the fluorescent versions thereof, fluorescent yellow-green, and fluorescent pink shall not be used as background colors for community wayfinding guide signs, in order to minimize possible confusion with critical, higher-priority regulatory and warning sign color meanings readily understood by road users. The minimum luminance ratio of legend to background for community wayfinding guide signs shall be 3:1.
All messages, borders, legends, and backgrounds of community wayfinding guide signs and any identification enhancement markers shall be retroreflective.
Guidance. Community wayfinding guide signs, exclusive of any identification enhancement marker used, should be rectangular in shape. Simplicity and uniformity in design, position, and application as described in EPG 903.2.6 are important and should be incorporated into the community wayfinding guide sign design and location plans for the area.
Community wayfinding guide signs should be limited to three destinations per sign.
Abbreviations should be kept to a minimum and should include only those that are commonly recognized and understood.
Horizontal lines of a color that contrasts with the sign background color should be used to separate groups of destinations by direction from each other.
Support. The basic requirement for all highway signs, including community wayfinding signs, is that they be legible to those for whom they are intended and that they be understandable in time to permit a proper response. EPG 903.2.14 contains additional information on the design of signs, including desirable attributes of effective designs.
Guidance. Word messages should be as brief as practical, and the lettering should be large enough to provide the necessary legibility distance.
Standard. The minimum specific ratio of letter height to legibility distance shall comply with the provisions of EPG 903.2.15. The size of lettering used for destination and directional legends on community wayfinding signs shall comply with the provisions of minimum letter heights as provided in EPG 903.7.6.
Interline and edge spacing shall comply with the provisions of EPG 903.7.6.
Except as provided below, the lettering style used for destination and directional legends on community wayfinding guide signs shall comply with the provisions of EPG 903.7.5.
The lettering for destinations on community wayfinding guide signs shall be a combination of lower-case letters with initial upper-case letters. All other word messages on community wayfinding guide signs shall be in all upper-case letters.
Option. A lettering style other than the Standard Alphabets provided in the “Standard Highway Signs and Markings” book may be used on community wayfinding guide signs if an engineering study determines that the legibility and recognition values for the chosen lettering style meet or exceed the values for the Standard Alphabets for the same legend height and stroke width.
Standard. Except for signs that are intended to be viewed only by pedestrians, bicyclists stopped out of the flow of traffic, or occupants of parked vehicles, Internet and e-mail addresses, including domain names and uniform resource locators (URL), shall not be displayed on any community wayfinding guide signs or sign assembly.
The arrow location and priority order of destinations shall follow the provisions described in EPG 903.7.8 and EPG 903.7.34. Arrows shall be of the designs provided in EPG 903.7.8.
Option. Pictographs may be used on community wayfinding guide signs.
Standard. If a pictograph is used, its height shall not exceed two times the height of the upper-case letters of the principal legend on the sign.
Except for pictographs, symbols that are not approved in the EPG for use on guide signs shall not be used on community wayfinding guide signs.
Business logos, commercial graphics, or other forms of advertising shall not be used on community wayfinding guide signs or sign assemblies.
Option. Other graphics that specifically identify the wayfinding system, including identification enhancement markers, may be used on the overall sign assembly and sign supports.
Support. An enhancement marker consists of a shape, color, and/or pictograph that is used as a visual identifier for the community wayfinding guide signing system for an area.
Option. An identification enhancement marker may be used in a community wayfinding guide sign assembly or may be incorporated into the overall design of a community wayfinding guide sign, as a means of visually identifying the sign as part of an overall system of community wayfinding signs and destinations.
Standard. The sizes and shapes of identification enhancement markers shall be smaller than the community wayfinding guide signs themselves. Identification enhancement markers shall not be designed to have an appearance that could be mistaken by road users as being a traffic control device.
Guidance. The area of the identification enhancement marker should not exceed 1/5 of the area of the community wayfinding guide sign with which it is mounted in the sign assembly.
903.7.50 Climbing Lane Signs (D17-1, D17-2) (MUTCD Section 2D.51)
Guidance. If an extra lane has been provided for trucks and other slow-moving traffic, a NEXT CLIMBING LANE XX MILES (D17-1) sign and/or a CLIMBING LANE XX MILES (D17-2) sign should be installed in advance of the lane.
Option. EPG 903.5.18 contains information regarding regulatory signs for these types of lanes.
903.7.51 National Scenic Byways Signs (D6-4) (MUTCD Section 2D.55)
Support. Certain roads have been designated by the U.S. Secretary of Transportation as National Scenic Byways or All-American Roads based on their archeological, cultural, historic, natural, recreational, or scenic qualities.
Table 903.7.51 lists the approved National Scenic Byways that follow state maintained routes.
Table 903.7.51 Approved National Scenic Byways in Missouri
| National Scenic Byways in Missouri |
|---|
| Crowley's Ridge Parkway |
| Little Dixie Highway of the Great River Road |
Option. National Scenic Byways (D6-4) signs may be installed at entrance points to a route that has been recognized by the U.S. Secretary of Transportation as a National Scenic Byway or an All-American Road. The D6-4 sign may be installed on route sign assemblies, see Fig. 903.7.51. National Scenic Byways signs may also be installed at periodic intervals along the designated route and at intersections where the designated route turns or follows a different numbered highway. At locations where roadside features have been developed to enhance the traveler’s experience such as rest areas, historic sites, interpretive facilities, or scenic overlooks, the National Scenic Byways sign may be placed on the associated sign assembly to inform travelers that the site contributes to the byway travel experience.
Standard. The National Scenic Byway signs shall be paid for by the group or association responsible for byway.
When a National Scenic Byways sign is installed on a National Scenic Byway or an All-American Road, the design shown for the D6-4 sign shall be used. Use of this design shall be limited to routes that have been designated as a National Scenic Byway or All-American Road by the U.S. Secretary of Transportation.
If used, the D6-4 sign shall be placed such that the roadway route signs have primary visibility for the road user.
Any additional signing, other than that provided by MoDOT, shall be located off of state maintained right of way.
903.7.52 Missouri Scenic Byways Signs (D6-4b, D6-4c, D6-4d)
Support. Certain roads have been designated by the Commission as Missouri Scenic Byways based.
Table 903.7.52 lists the approved Missouri Scenic Byways that follow state maintained routes.
Option. Missouri Scenic Byways signs may also be installed at periodic intervals along the designated route.
Table 903.7.52 Approved Missouri Scenic Byways
At locations where roadside features have been developed to enhance the traveler’s experience, the Missouri Scenic Byways Point of Interest (D6-4d) plaque may be placed below the Missouri Scenic Byway (D6-4b) sign to inform travelers that the site contributes to the byway travel experience.
The end of the byway may be marked with the Missouri Scenic Byways (D6-4c) Confirmation sign with the END (M4-6) auxiliary sign mounted below.
Standard. The Missouri Scenic Byway (D6-4b) signs shall be installed at the beginning of the byway and shall include the byway name at the bottom of the sign.
Missouri Scenic Byways (D6-4c) Confirmation signs shall be installed above route turn assemblies and at intersections where the designated route turns or follows a different numbered highway.
When a Missouri Scenic Byways sign is installed on state maintained routes, the design shown for the D6-4b or D6-4c sign shall be used. Use of this design shall be limited to routes that have been designated as a Missouri Scenic Byway by the Commission.
If used, the D6-4b or D6-4c sign shall be placed such that the roadway signs have primary visibility for the road user.
Any additional signing, other than that provided by MoDOT, shall be located off state maintained right of way.
Support. In some instances, a Missouri Scenic Byway will receive National Scenic Byway status in which case the byway is eligible for additional signing to denote this designation and is eligible for first order signing.
Standard. If a Missouri Scenic Byway receives National Scenic Byway status, the National Scenic Byways (D6-4a) sign shall be mounted below the Missouri Scenic Byway (D6-4b) sign or the Missouri Scenic Byways (D6-4c) Confirmation sign.
If a Missouri Scenic Byway receives National Scenic Byway status it is eligible for first order signing.
First order signing for at grade intersections shall consist of a Public Use Area (D7-10) sign containing the byway name, the National Scenic Byway logo and a directional arrow and a distance, if applicable, to the beginning of the byway if less than one mile.
For grade-separated interchanges, supplement guide signs and ramp signing may be installed to direct traffic to the byway. The mainline signs shall be white on brown and contain the America’s Byway logo, the name of the byway and NEXT RIGHT. The ramp sign will be of the same design as the first order at grade signing.
The location of these signs shall be identical to that found on a normal Missouri Scenic Byway. The costs associated with the National Scenic Byways designation shall be the responsibility of the group or association responsible for byway.